RFID Reader in Mobile: Can a Phone Really Do the Job?
17RFID reader in mobile devices explained with real use cases, limits, and solutions. Learn how professionals use mobile RFID readers with CYKEO.
MoreAll RFID Product
An RFID scanner might seem like a simple handheld gadget, but it’s the linchpin of modern tracking systems. From ensuring your online orders ship on time to safeguarding hospital equipment, these devices turn invisible radio waves into actionable data. But what exactly makes them tick, and why are they indispensable across industries? Let’s demystify RFID scanners and their game-changing capabilities.
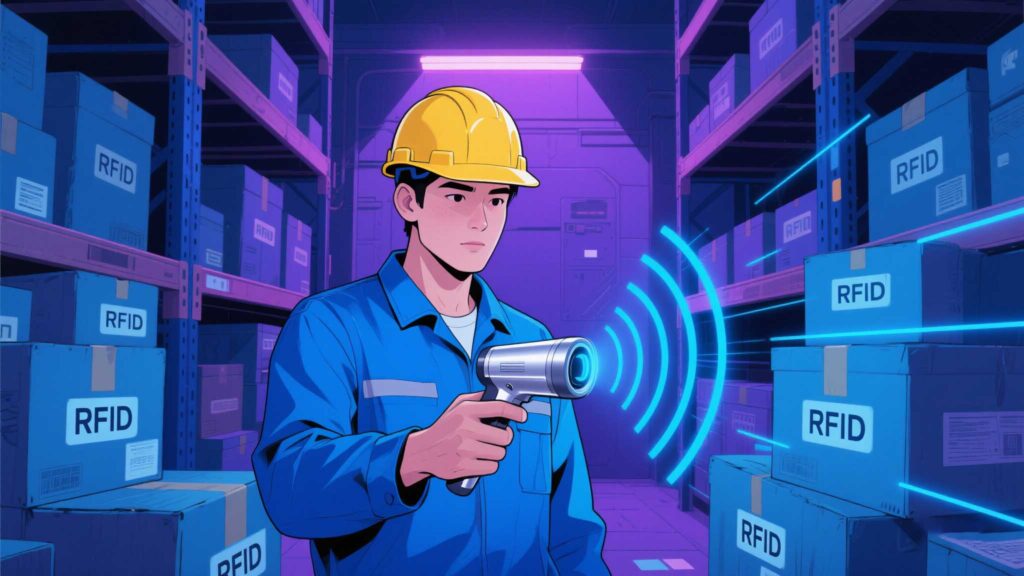

An RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification) scanner is a device that wirelessly communicates with RFID tags to capture and transmit data. Unlike barcode scanners requiring line-of-sight, RFID scanners can read multiple tags simultaneously through obstacles like boxes, fabric, or plastic.
Key Components:
Example: In a Cykeo-equipped warehouse, scanners read tags on pallets 10 meters away, updating stock levels in real time without manual checks.
A. By Mobility:
B. By Frequency:
| Type | Range | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| LF | 0–10 cm | Livestock tracking, car keys |
| HF | 10 cm–1 m | Library books, payment cards |
| UHF | 1–15 m | Warehousing, retail inventory |
C. By Power Source:
Cykeo’s Edge: Their UHF scanners excel in high-interference areas like metal-heavy factories, achieving 99% read accuracy.
Ask These Questions:
Pro Tip: For mixed environments, use hybrid scanners that support multiple frequencies.
Takeaway: RFID scanners are the silent workhorses of automation, bridging the physical and digital worlds. Whether you’re a small retailer or a global manufacturer, understanding their capabilities—and limits—is key to building faster, leaner, and error-proof workflows.
RFID reader in mobile devices explained with real use cases, limits, and solutions. Learn how professionals use mobile RFID readers with CYKEO.
MoreProtect your RFID reader network from cyberattacks with encryption, access controls, and Cykeo’s security tools. Learn how to safeguard data and prevent breaches.
MoreHow to use RFID on iPhone for real UHF applications. Learn how CYKEO’s Bluetooth RFID reader enables long-range RFID scanning on iOS.
MoreLearn how to protect data in long-range RFID networks from interception or tampering. Discover Cykeo’s encryption, authentication, and compliance strategies for secure operations.
More