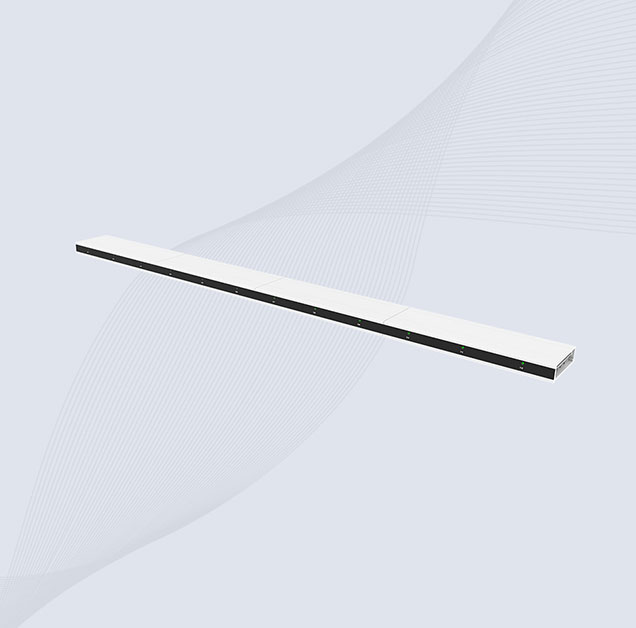
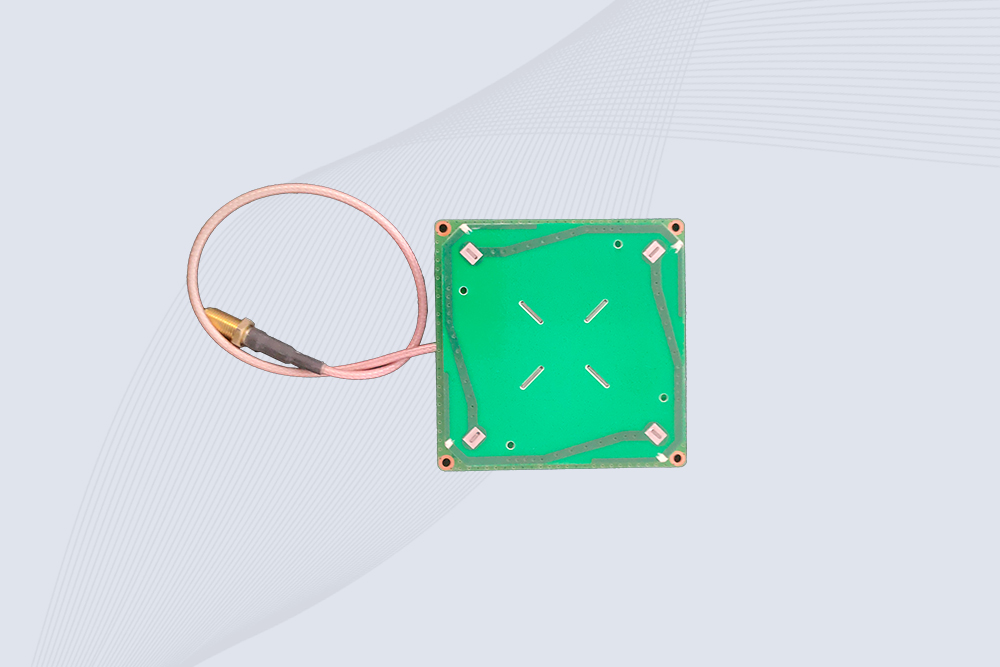
Cykeo RFID Antennas
Cykeo supplies RFID antennas covering 3 dBi, 6 dBi, 9 dBi and 12 dBi gain options, designed for use with Fixed RFID Readers or RFID Modules.
The antenna range includes HF and UHF RFID antennas, suitable for access control, asset identification, smart cabinets, RFID gates and other system-level applications.
All Cykeo RFID antennas are developed as part of a complete hardware solution. When paired with Cykeo fixed readers or embedded RFID modules, they support stable tag reading and predictable coverage. SDKs, APIs and demo software are available for system integration, allowing customers to focus on software logic rather than low-level RF handling.

More about RFID Antennas
Cykeo carry a wide range of antennas to fit an equally wide range of tags, readers, and systems. This includes HF antennas, UHF antennas, patch antennas, and linear or circular polarized antennas. Each antenna has different strengths, and each fits specific types of RFI systems. We’re here to help assist you in selecting the best RFID antenna for your application
Cykeo offer a very strong after-sales team and rapid technical support services, including support for SDKs, APIs, software integration, system development, mobile or desktop applications, as well as any related configuration or troubleshooting assistance, making your project very convenient from planning to implementation.
More About UHF RFID Antennas
UHF RFID antennas are used when reading distance, coverage area, and read speed matter more than close control. In many warehouse and logistics projects, the antenna—not the reader—is what really defines how the system performs. Cykeo UHF RFID antennas are designed to create stable and predictable read zones, helping systems capture tag data as pallets, cartons, or assets move through a space.
These antennas are commonly installed at dock doors, conveyor lines, storage aisles, or production checkpoints. Different gain levels and polarization options allow installers to adapt to metal structures, narrow passages, or wide open areas. With solid enclosures and flexible mounting options, Cykeo UHF RFID antennas support long-term operation in busy industrial and commercial environments where consistency matters more than peak lab performance.
At Cykeo, we offer a wide range of RFID readers to suit various applications and industries. From handheld RFID readers, USB RFID readers, Long Range RFID Reader, Portable RFID Reader, RFID Gate Reader, and fixed RFID readers to multi-functional, multi-frequency options, our carefully developed product portfolio provides RFID hardware for any type of system and project. Whether you’re upgrading your supply chain operations or enhancing workplace security, our RFID readers deliver reliability, precision, and performance to meet your business needs.
More About HF RFID Antennas
HF RFID antennas are typically chosen for applications where reading accuracy and control are more important than distance. Cykeo HF RFID antennas are used in systems where tags are intentionally presented to a specific location, such as access points, desks, counters, cabinets, or embedded equipment. Their shorter read range helps prevent unintended tag detection in crowded environments.
Because HF systems often interact with one tag at a time, antenna stability is critical. Cykeo designs its HF RFID antennas to maintain a consistent magnetic field, reducing read errors caused by misalignment or nearby electronics. Compact form factors make them easy to integrate into finished products or enclosed systems. These antennas are widely used in authentication, identification, and secure data exchange applications where reliability and precision are essential.
Frequently Asked Questions:RFID Antennas
In real RFID projects, the antenna is often the most underestimated part. An RFID antenna is the component that actually pushes radio energy into space and listens for the tag’s response. The reader handles logic and data, but the antenna defines where reading happens.
In practice, antennas are used to shape a read zone. That zone could be a doorway, a tabletop, or a narrow conveyor path. At Cykeo, many performance issues traced back to antenna choice rather than reader model. A strong reader with the wrong antenna placement will still miss tags. That is why antenna selection usually comes early in system design, not at the end.
An RFID antenna works by converting electrical signals from the reader into radio waves and then converting incoming reflections back into signals the reader can understand. When powered, the antenna creates a field. Any tag inside that field may respond.
What matters in daily use is how stable that field is. Reflections from metal, moving objects, or nearby antennas can distort it. Cykeo antennas are designed to maintain predictable signal patterns, which reduces unexpected reads. The antenna does not “think,” but it strongly influences read reliability. Poor antenna orientation can turn a good system into an unreliable one very quickly.
There is no reliable “average” range for an RFID reader and antenna. On paper, UHF systems may claim long distances, but real environments rarely match those conditions. In warehouses, effective ranges are often between 3 and 8 meters.
HF systems operate much closer, usually within a few centimeters, by design. Tag size, mounting surface, antenna gain, and surrounding materials all affect results. At Cykeo, range is tested on site, not assumed from datasheets. In many cases, limiting range improves accuracy. Too much coverage often causes more problems than it solves.
Choosing an RFID antenna starts with the environment, not the reader. Ceiling height, metal structures, tag orientation, and how items move all matter. An antenna that works well on a desk may fail at a dock door.
Polarization is another key factor. Circular polarization helps when tag orientation changes. Linear polarization is stronger but less forgiving. Cykeo engineers often test two or three antenna types before finalizing a setup. This saves time later. A well-chosen antenna reduces software filtering and troubleshooting effort during operation.
Yes, RFID readers need antennas to function. Without an antenna, the reader cannot transmit or receive radio signals. Some readers have built-in antennas, but most professional systems rely on external ones.
External antennas give better control over coverage and placement. They allow the reader to be installed safely while antennas are positioned exactly where reading is required. Cykeo systems commonly use multiple antennas connected to one reader to cover different zones. The antenna is not optional; it is fundamental to the system working at all.
An RFID antenna enables multiple tags to be read, but the reader manages the process. In UHF systems, the antenna creates a field where many tags respond simultaneously. The reader then separates those responses.
A poorly designed antenna can cause uneven signal strength, making some tags respond repeatedly while others are missed. Cykeo antennas are tuned to create balanced coverage, which helps readers handle high tag density. This is why antenna quality matters during inventory counts, where dozens of tags may be present in the same space.
RFID antennas can be very small, but size always affects performance. HF antennas can be compact because they work at close range. UHF antennas generally need more physical space to operate efficiently.
In embedded systems, designers often push for smaller antennas, but this comes with trade-offs. Reduced range and sensitivity are common. Cykeo typically advises against choosing the smallest possible antenna unless the application truly requires it. Stability and consistency are usually more valuable than saving a few centimeters of space.
An RFID antenna never connects directly to software. It connects to the reader using RF cables. The reader then communicates with software through Ethernet, USB, or wireless links.
In software, the antenna is treated as a port or channel. Power levels, timing, and read behavior are configured there. Cykeo systems allow each antenna port to be controlled independently. This lets users fine-tune read zones without changing hardware. Correct antenna configuration in software is just as important as physical installation.
HF and UHF RFID antennas serve very different purposes. HF antennas are used for short-range, intentional interactions, where only one tag should be read. They are common in access control and authentication.
UHF antennas are designed for distance and volume. They can read many tags at once and cover larger areas. Cykeo recommends choosing based on behavior, not technology preference. If you need control, HF is usually better. If you need speed and coverage, UHF is the practical choice.
An antenna RFID reader usually refers to a reader that relies on external antennas instead of an internal one. This setup is common in industrial systems.
External antennas allow flexible placement. The reader can be mounted in a protected enclosure, while antennas are installed where tags pass. Cykeo uses this structure in gates, tunnels, and production lines. It improves durability and makes maintenance easier. The antenna-reader separation is often what enables reliable long-term operation.
The reader sends energy to the antenna, which radiates it outward. Tags in the field absorb that energy and respond with data. The antenna captures the response and sends it back to the reader.
This exchange happens very quickly and repeatedly. The antenna’s job is to keep the signal clean and stable. Cykeo designs antenna layouts based on real tag movement, not static tests. When antenna and reader are well matched, reads become predictable rather than random.
Testing an RFID antenna reader is mostly practical work. Known tags are scanned at different positions and orientations. Read consistency matters more than peak distance.
Environmental testing is critical. Nearby metal, forklifts, or people can change results. Cykeo recommends testing antennas after final installation, not before. Software logs are checked for missed or duplicate reads. A system that performs well in real conditions will usually remain stable over time.
Impinj RFID antennas are designed for consistent UHF performance rather than extreme range. In real deployments, effective distances are commonly between 3 and 10 meters.
Actual results depend on reader power, tag sensitivity, and environment. Cykeo projects using Impinj-based systems usually tune antennas to fit the site layout instead of pushing maximum power. This approach reduces false reads and improves long-term reliability. Field testing always matters more than published numbers.
An RFID reader with antenna refers to a complete system capable of transmitting and receiving tag data. The antenna may be internal or external.
External antennas are preferred in professional installations because they offer better control. Cykeo reader-and-antenna combinations are selected together to ensure compatibility. When matched correctly, the system delivers stable reads and complies with regional RF regulations. Treating the reader and antenna as a pair avoids many common deployment problems.
RFID antenna cables carry high-frequency signals, and their quality matters. Poor cables cause signal loss, unstable reads, and intermittent failures.
Cable length, shielding, and connector quality all affect performance. Cykeo recommends keeping cables as short as possible and using properly rated RF cables. In industrial environments, mechanical durability is also important. A good antenna with a bad cable will still perform poorly.
RFID antennas are used wherever tag detection needs to be controlled. Common scenarios include dock doors, conveyors, access points, cabinets, and workstations.
They are also embedded in machines and kiosks. Cykeo antennas are used in both permanent installations and semi-mobile setups. Any system that needs reliable, repeatable RFID reads depends on the antenna to define behavior. In many cases, the antenna shapes the system more than the reader itself.
 Cykeo RFID IoT Solution Products R&D Manufacturer
Cykeo RFID IoT Solution Products R&D Manufacturer