Why Are Modular RFID Readers Gaining Popularity in 2024?
939Discover why modular RFID readers are trending in 2024. Learn how flexibility, scalability, and Cykeo’s innovations make them essential for modern industries.
MoreAll RFID Product
RFID systems generally operate in three frequency bands: Low Frequency (LF), High Frequency (HF), and Ultra High Frequency (UHF). For B2B scenarios like industrial automation, logistics tracking, and warehouse management, most fixed RFID readers use either HF (13.56MHz) or UHF (902–928MHz).
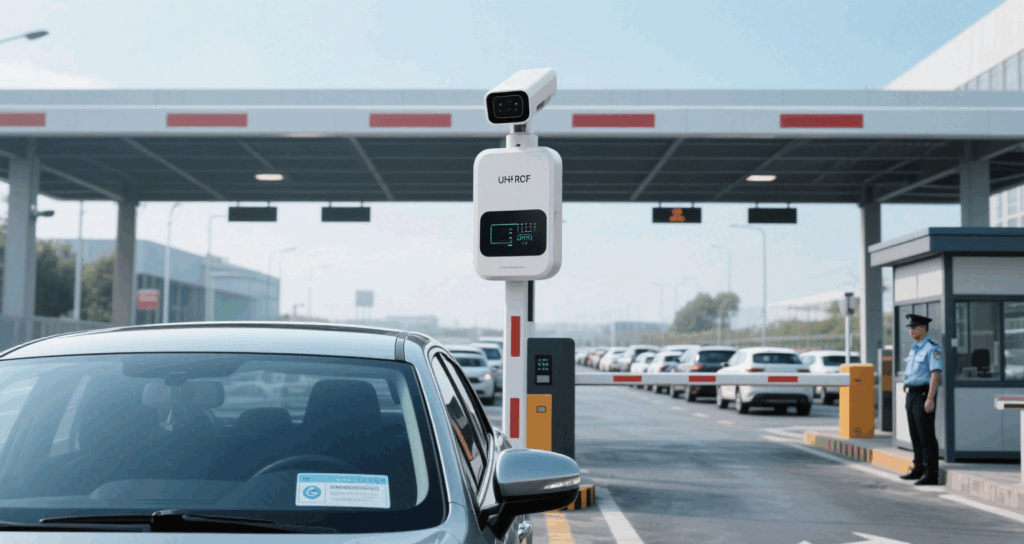

Reading distance is one of the most critical RFID reader specs. HF typically reads within 10 cm, while UHF can reach over 10 meters. When buying reader, consider these factors:
For projects like warehouse entry/exit control, vehicle ID, and asset tracking, define both the minimum and maximum read range requirements, and choose a reader with adjustable output power.
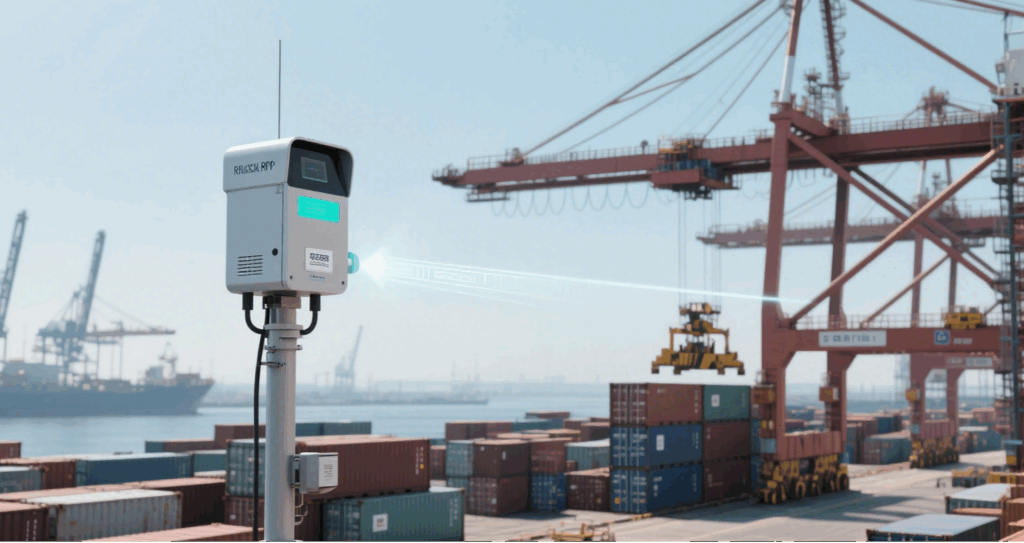

The reader’s output power—usually from 0 to 30 dBm—directly affects both reading distance and energy efficiency. Choose a model that supports power adjustment to handle:
Industrial-grade RFID readers should support multiple interfaces for system integration. Common interface types include:
Clarify your system’s integration needs and choose a reader with versatile interface options.
A fixed RFID reader’s operating mode determines how it controls the scanning process. Common modes include:
Choose reader that supports multiple operating modes and remote configuration for greater flexibility in future expansions.
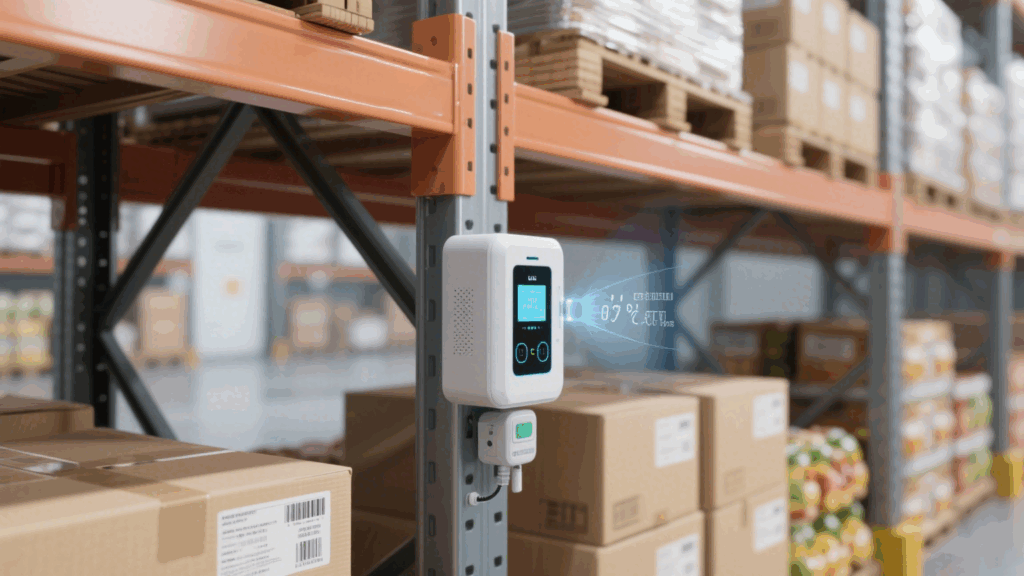

When purchasing fixed RFID reader, evaluate it across five key areas: frequency compatibility, read range, power control, interface type, and operating mode. Industrial-grade models that support multi-protocols, multiple interfaces, remote configuration, and adjustable power offer the best flexibility for complex deployment needs.
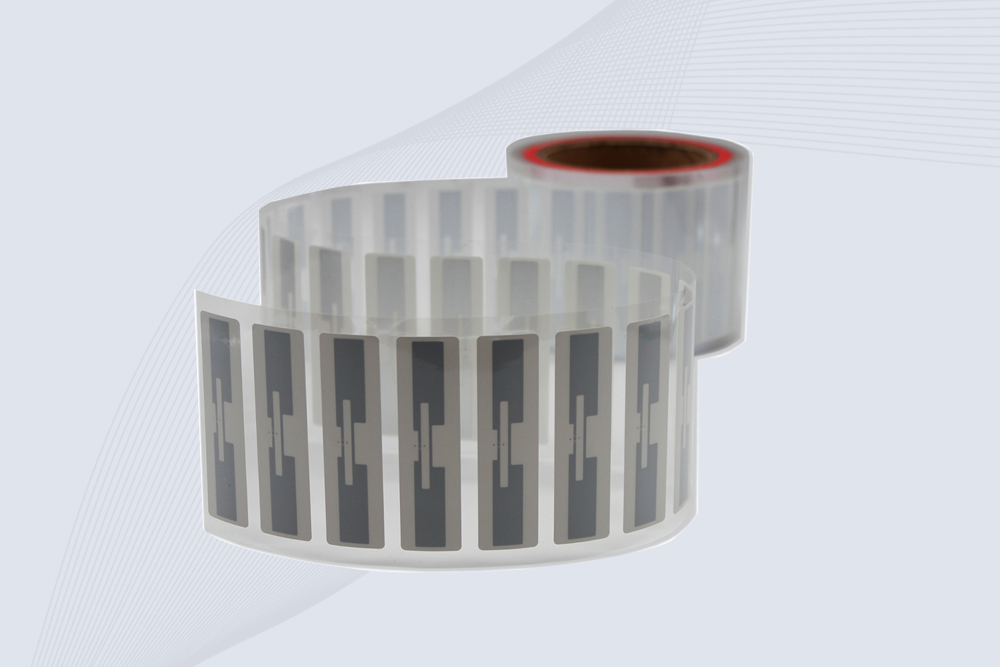
CYKEO Passive RFID Tags are made for wet and high-humidity environments where standard labels do not last. This rfid passive tag is often used around liquids, chemicals and temperature changes, providing stable reading distance and long data life for industrial tracking.
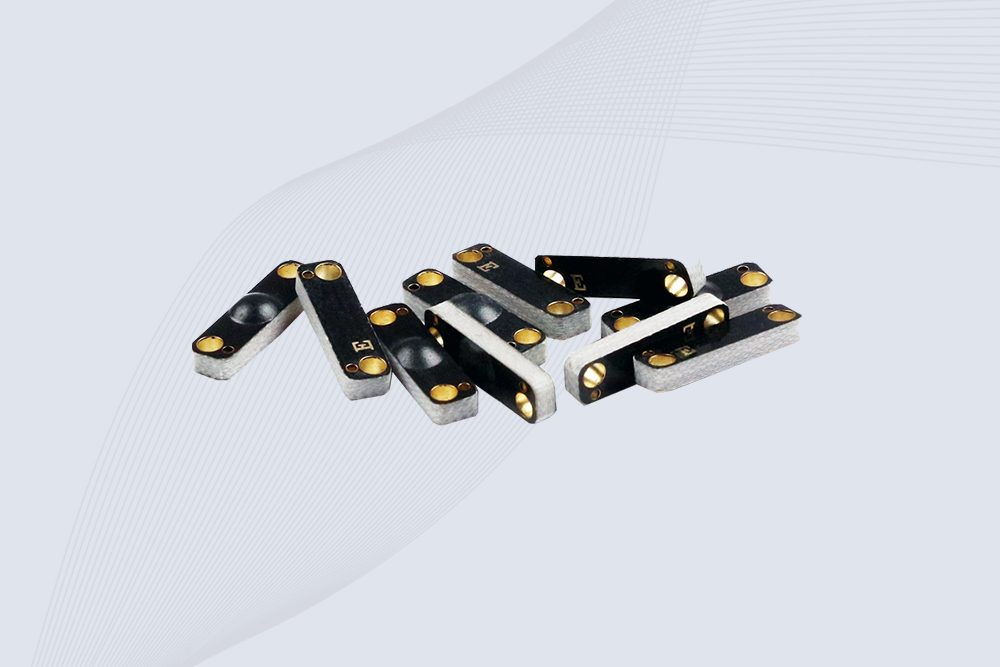

CYKEO CK-BQ1504 Metal RFID Tags is a compact anti-metal UHF RFID solution built for direct mounting on metal surfaces. With stable 8-meter read range, Ucode-8 chip, and long data retention, this rfid metal tag fits tools, containers, automotive parts, and industrial asset tracking.
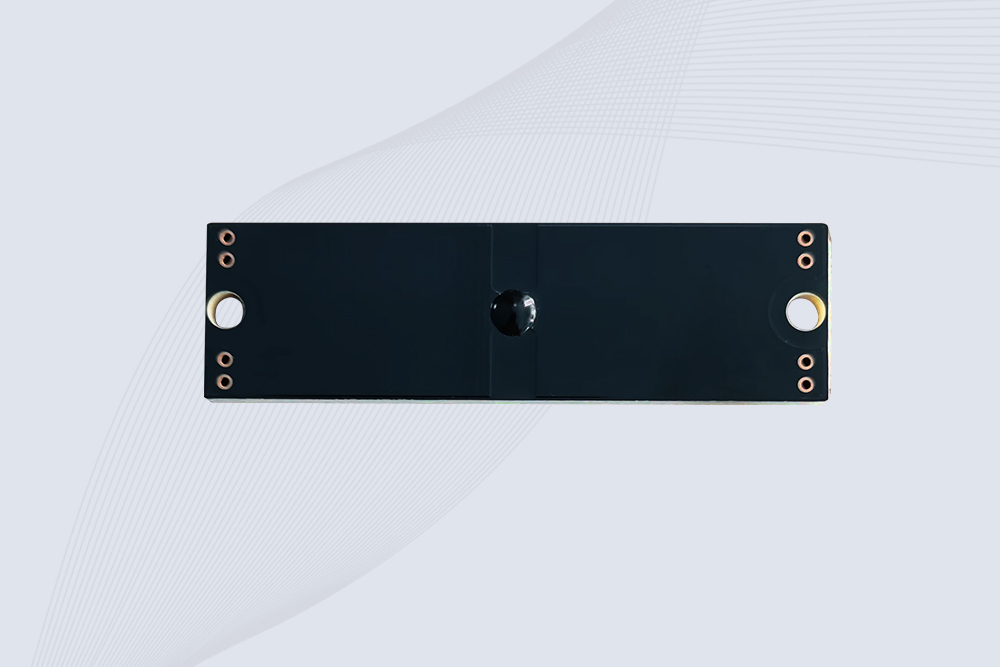

CYKEO CK-BQ7020 On-Metal RFID Tags are designed for reliable tracking on steel and metal surfaces. Built with an FR4 epoxy body and industrial-grade chips, these On-Metal RFID Tags deliver stable performance, long data life, and chemical resistance, making them a dependable RFID anti-metal tag for harsh environments.
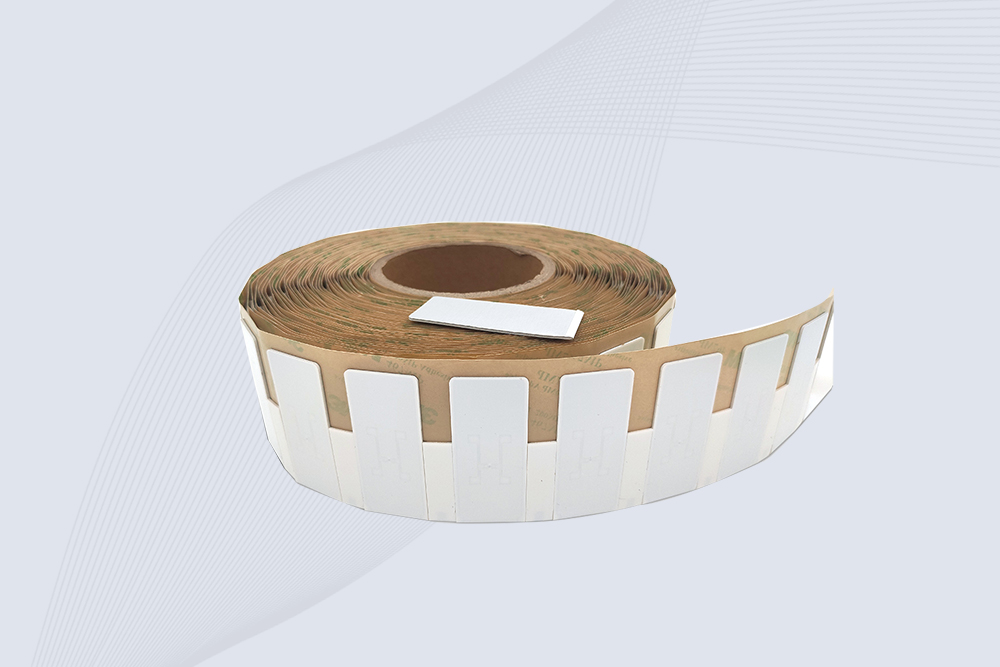
The CYKEO CK-BQ6025 Anti-Metal RFID Tag is built for metal surfaces where standard tags fail. Designed for long-range performance, harsh environments, and stable data retention, this Anti-Metal RFID Tag is ideal for industrial assets, containers, and equipment tracking using on metal RFID tags.
Discover why modular RFID readers are trending in 2024. Learn how flexibility, scalability, and Cykeo’s innovations make them essential for modern industries.
MoreDiscover what an RFID reader is used for in logistics, retail, manufacturing, and security. Learn how CYKEO’s RFID solutions enhance efficiency and accuracy.
MoreDiscover the cost benefits of fixed RFID readers vs. barcode systems. Learn how Cykeo’s RFID solutions reduce labor, errors, and long-term expenses in warehouses and retail.
Morehow RFID gate systems provide contactless, automated access for residential, commercial, and industrial sites. Explore UHF RFID readers and integration options.
More