Can Budget RFID Scanners Accurately Track Retail Apparel Inventory?
1164Find out if budget RFID scanners can handle retail apparel inventory tracking. Compare accuracy, UHF performance, and top affordable models for clothing stores.
MoreAll RFID Product
If you’ve ever tried to choose the right RFID tag for a project, you’ll know it’s never as simple as it sounds. On paper, everything looks straightforward — active, passive, semi-passive; LF, HF, UHF — just a few categories. But when you’re standing in a warehouse or production line trying to figure out why some tags read perfectly while others act like they’re invisible, you start to realize that these classifications actually define the soul of the system.
So let’s break it down — not as theory, but the way people in the field understand it.
The first and most important way to classify RFID tags is by power source — that tiny detail decides how a tag behaves, how far it talks, and how much it costs you in the long run.
Passive tags are the quiet workers of the RFID world. They don’t have a battery; instead, they borrow power from the reader’s electromagnetic field. Think of them as people who speak only when spoken to — they wait for a signal, gather a bit of energy from it, and send back their data.
They’re cheap, compact, and maintenance-free. You can tag thousands of boxes or apparel items and forget about them for years. But there’s a trade-off — their read range is short, and they don’t like metal or water too much. In warehouses with reflective surfaces or cold-chain packaging, their performance can drop fast if not properly tuned.
Then there’s the middle ground — semi-passive or “battery-assisted” tags. These have a small built-in battery that powers the chip but still rely on the reader’s signal to talk back. You can think of them like someone who’s half-asleep but wakes up instantly when you call their name.
They offer better range, more stable performance, and even allow sensor functions like temperature or humidity logging. They’re popular in logistics, cold chain, and industrial monitoring, where reliability matters more than saving a few cents per tag. The only downside? You’ll eventually have to replace the battery.
Active tags are in a league of their own. They have a full battery and transmitter, meaning they can speak up anytime — even shout across a warehouse or yard. They’re used for long-distance tracking, real-time location systems, and monitoring expensive assets like vehicles or medical equipment.
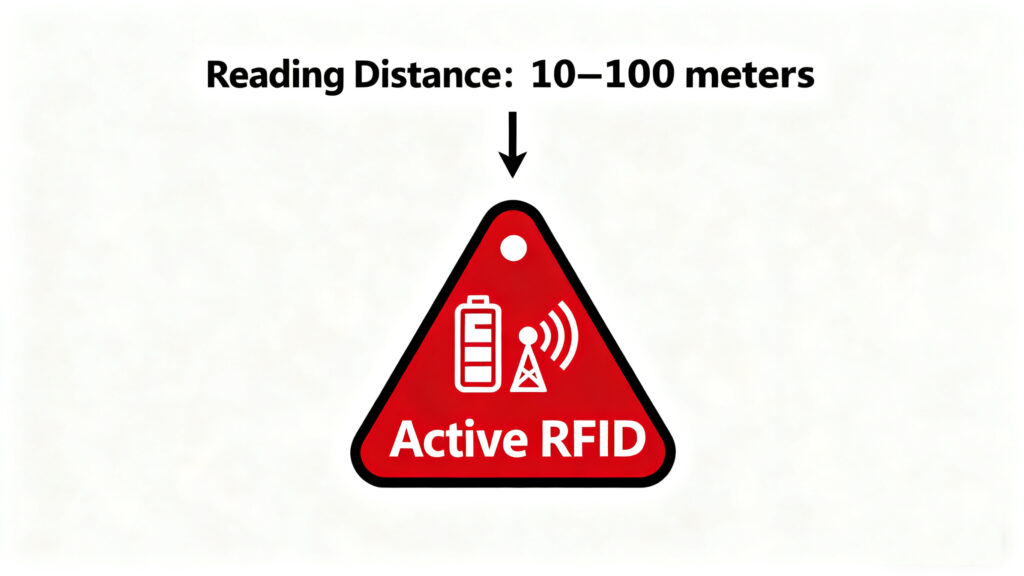
They’re powerful but also more expensive and bulkier. You don’t want to use these on individual retail items, but for tracking a shipping container or a forklift, they’re perfect. Just be prepared for periodic maintenance — no battery lasts forever.
Once you understand power types, the next layer in the classification of RFID tags comes down to frequency — the “channel” through which data travels. Each frequency band has its own personality.
LF tags operate around 125 kHz. They work slowly, with short read ranges (usually under 30 cm), but they’re tough. They don’t care much about water, metal, or dust, which makes them great for animal tracking or access control systems where reliability beats range.
HF, around 13.56 MHz, sits in the middle. It’s used in contactless cards, library systems, and NFC interactions. The range is modest — about one meter or less — but it’s stable and easy to integrate into consumer devices. If you’ve ever tapped your phone to a gate or a payment terminal, you’ve used HF RFID.
UHF tags are the rock stars of logistics. Operating between roughly 860 and 960 MHz, they offer much longer read ranges — several meters or even tens of meters with the right setup. They can read hundreds of tags in seconds, which makes them ideal for supply chains, retail, and warehouse automation.
The only catch is that UHF doesn’t like reflective or moist environments. Metal shelves, liquids, and tight spaces can distort the signal. But with proper tag selection and antenna placement, it’s still the most versatile frequency for large-scale deployments.
So how do you actually decide which tag fits your project? Forget the fancy datasheets for a moment and think about what you’re trying to achieve:
Choosing the right RFID tag isn’t just about frequency or battery — it’s about matching technology with the physical reality of your operation.
A tag that works perfectly in a lab might fail miserably on a metal rack in a cold warehouse. Similarly, a long-range active tag might be overkill for a small retail space where the goal is just to confirm items near a counter.
That’s why understanding the classification of RFID tags is less about memorizing terms and more about learning their behavior — how they interact with the real world. Once you know that, you can build systems that don’t just work, but work consistently.

RFID technology is like a toolbox — every tag type has its purpose. Classifying them by power and frequency helps narrow down the options, but the magic lies in knowing when to mix and match.
In the end, the right choice isn’t the most expensive one or the most advanced one — it’s the one that fits your application, environment, and budget like a glove.
CYKEO Passive RFID Tags are made for wet and high-humidity environments where standard labels do not last. This rfid passive tag is often used around liquids, chemicals and temperature changes, providing stable reading distance and long data life for industrial tracking.
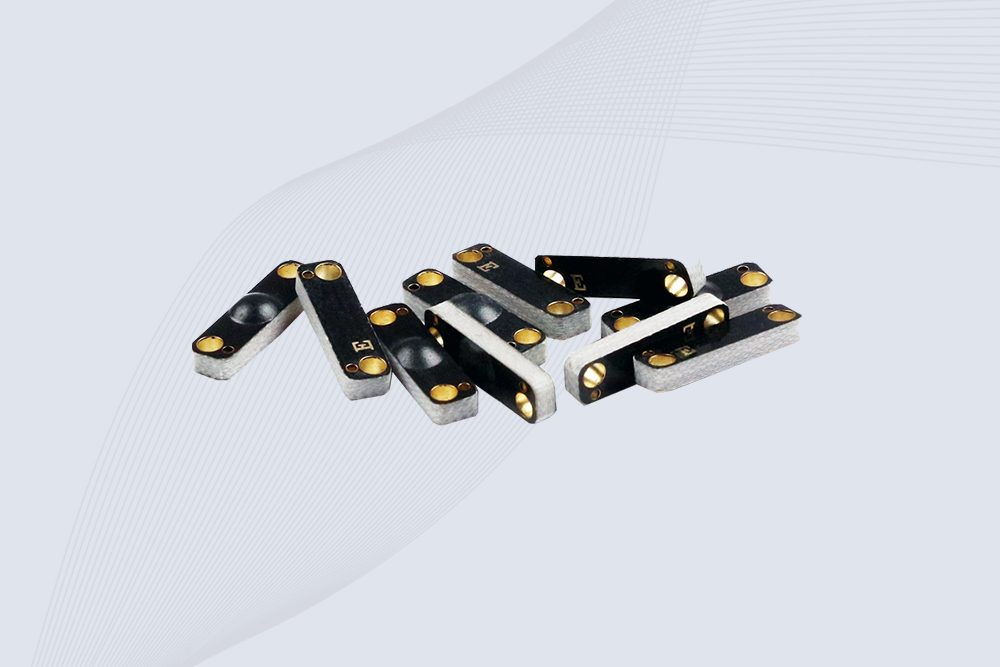

CYKEO CK-BQ1504 Metal RFID Tags is a compact anti-metal UHF RFID solution built for direct mounting on metal surfaces. With stable 8-meter read range, Ucode-8 chip, and long data retention, this rfid metal tag fits tools, containers, automotive parts, and industrial asset tracking.
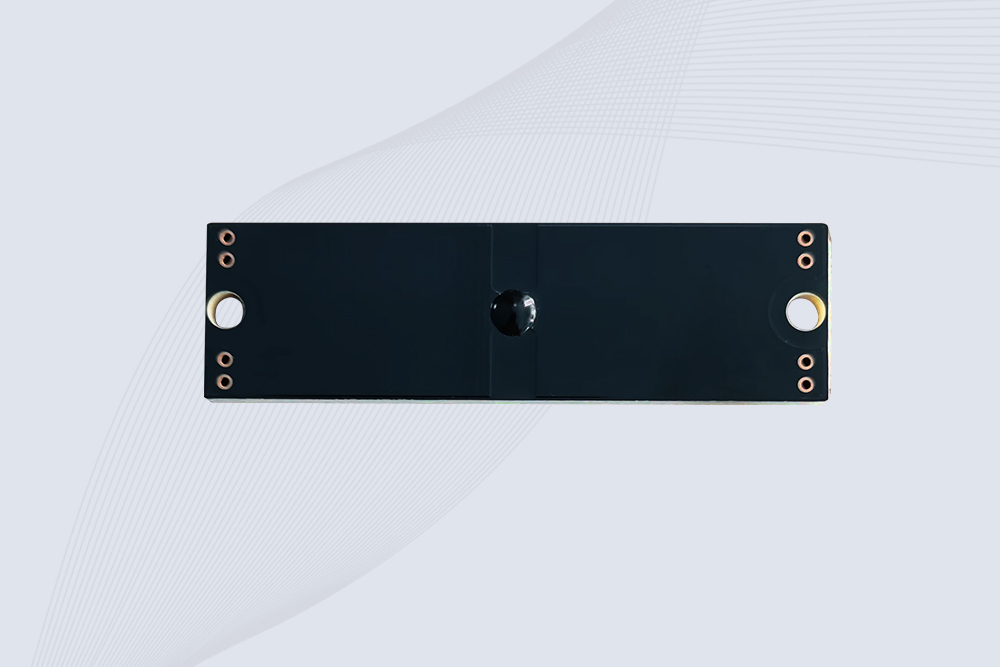

CYKEO CK-BQ7020 On-Metal RFID Tags are designed for reliable tracking on steel and metal surfaces. Built with an FR4 epoxy body and industrial-grade chips, these On-Metal RFID Tags deliver stable performance, long data life, and chemical resistance, making them a dependable RFID anti-metal tag for harsh environments.
The CYKEO CK-BQ6025 Anti-Metal RFID Tag is built for metal surfaces where standard tags fail. Designed for long-range performance, harsh environments, and stable data retention, this Anti-Metal RFID Tag is ideal for industrial assets, containers, and equipment tracking using on metal RFID tags.
Find out if budget RFID scanners can handle retail apparel inventory tracking. Compare accuracy, UHF performance, and top affordable models for clothing stores.
MoreRFID CFS systems integrate RFID technology with container freight station (CFS) management to enable automatic cargo identification, real-time tracking, and full process visibility, helping logistics companies enhance efficiency, reduce costs, an...
MoreDiscover how handheld RFID scanners reduce shipping mistakes, improve accuracy, and streamline logistics workflows. Learn best practices for implementation.
Morein-depth breakdown of the entire RFID tag testing process—from design validation to real-world field trials—featuring warehouse and Arduino case studies. Covers practical methods for testing read range, orientation sensitivity, interference resis...
More