Can You Use an NFC Phone as an RFID Tag?
1288Discover whether NFC phones can function as RFID tags, how NFC-RFID integration works, and Cykeo’s solutions for cross-technology applications.
MoreAll RFID Product
The first time you buy RFID tags, you probably don’t have much of an idea. Most people just think, “Isn’t it just a sticker?” But when you actually need to purchase, the real questions come: which type should I buy? Will it fail on metal surfaces? Can it survive in cold storage? Do I need one with a battery?
These little questions become a lot bigger once they’re tied to thousands of assets.
I’ve been around RFID for a few years now. My first encounter was in a logistics warehouse project. I still remember the moment I saw a whole row of shelves scanned in seconds by an RFID reader—it was a bit shocking. That’s when I realized RFID tags aren’t just “barcode replacements,” they’re more like tiny smart chips that can slip into almost any scenario.

There are more varieties of RFID tags on the market than you might think. Generally, they fall into these categories:
They might all look similar at first glance, but once you drop them into a specific environment, the differences show immediately.

The core of an RFID tag is its frequency and chip. Different frequencies are like different car models—each with its strengths.
And beyond frequency, the functions keep getting more specialized:
That’s why, when people buy tags, they don’t just go for the cheapest option—they go for what fits their environment.
When we talk about buying RFID tags, price always comes up. Someone will say, “Aren’t they just a few cents each?” That’s true—but only for the most basic passive tags. Once you scale up or enter special environments, the price gap widens fast.
Factors that affect cost:
I’ve seen companies try to cut costs with cheap tags, only to have them fail within a week on high-temperature production lines. They ended up buying high-temp ones anyway. In the end, the “expensive” choice turned out cheaper overall.
No matter how you buy RFID tags, three things matter most:
In tough environments, a good tag can last years. A bad one might fail in days.
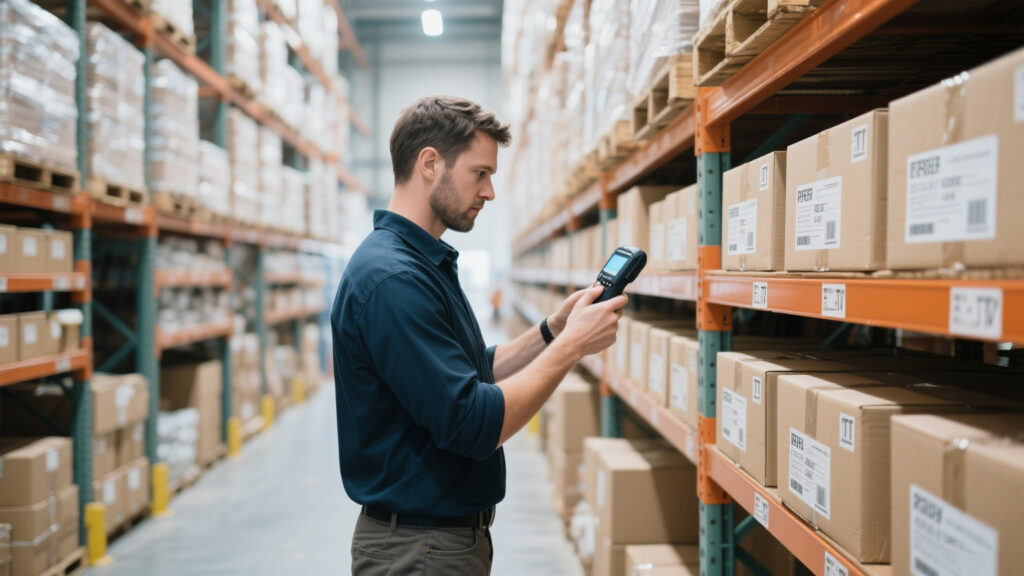

Still unsure which RFID tag you need? Look at these scenarios:
I once visited a repair company that tagged every tool with RFID. Workers scanned tools at check-out and check-in. Overnight, their lost-tool rate dropped by 70%. Such a small change, but the impact was way beyond what they expected.
When you’re ready to buy RFID tags, don’t just look at the price tag. Think carefully: what environment will you use them in, how often, and what problem are you solving? Then pick the right type and supplier.
RFID tags may look like tiny stickers, but they can make warehouses smarter, hospitals safer, and retail more efficient. The right tag is a true helper; the wrong one is nothing but wasted paper.
The best advice? Get samples first and test. Don’t think of it as a hassle—the money you spend on a trial might save you a year’s worth of headaches.
CYKEO Passive RFID Tags are made for wet and high-humidity environments where standard labels do not last. This rfid passive tag is often used around liquids, chemicals and temperature changes, providing stable reading distance and long data life for industrial tracking.
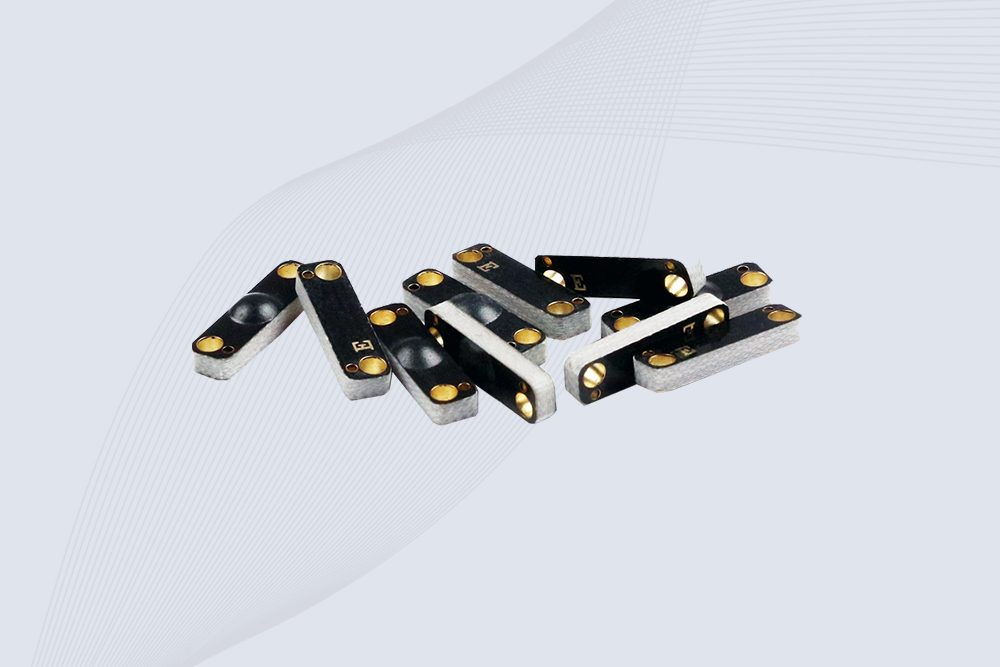

CYKEO CK-BQ1504 Metal RFID Tags is a compact anti-metal UHF RFID solution built for direct mounting on metal surfaces. With stable 8-meter read range, Ucode-8 chip, and long data retention, this rfid metal tag fits tools, containers, automotive parts, and industrial asset tracking.
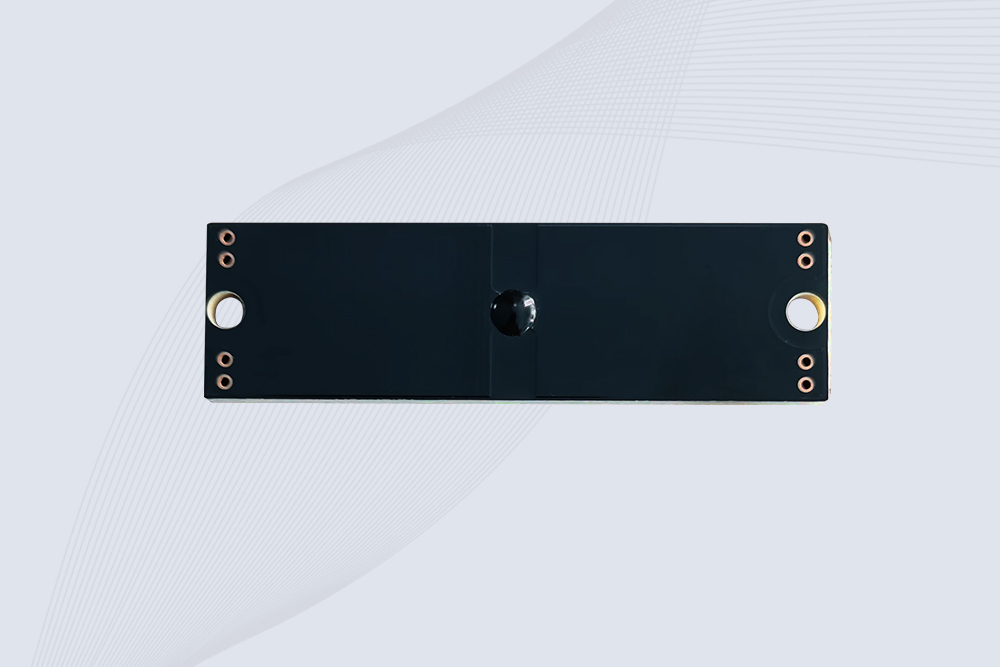

CYKEO CK-BQ7020 On-Metal RFID Tags are designed for reliable tracking on steel and metal surfaces. Built with an FR4 epoxy body and industrial-grade chips, these On-Metal RFID Tags deliver stable performance, long data life, and chemical resistance, making them a dependable RFID anti-metal tag for harsh environments.
The CYKEO CK-BQ6025 Anti-Metal RFID Tag is built for metal surfaces where standard tags fail. Designed for long-range performance, harsh environments, and stable data retention, this Anti-Metal RFID Tag is ideal for industrial assets, containers, and equipment tracking using on metal RFID tags.
Discover whether NFC phones can function as RFID tags, how NFC-RFID integration works, and Cykeo’s solutions for cross-technology applications.
MoreDiscover why hospitals rely on portable RFID readers for medical equipment tracking. Learn about real-time visibility, cost savings, and compliance with healthcare standards.
MoreDiscover the top UHF RFID scanners for warehouse inventory tracking in 2025. Compare range, durability, software integration, and future-ready features for logistics efficiency.
MoreNFC tags vs RFID: Understand range, cost & use cases. Learn when NFC’s phone compatibility beats RFID’s industrial power. No jargon, just clear answers.
More