The Real Cost of Owning a Handheld RFID Scanner: Breaking Down Expenses and ROI
934Discover the hidden costs of handheld RFID scanners—hardware, software, maintenance, and more. Learn how to calculate ROI and avoid budget surprises.
MoreAll RFID Product
If you’ve ever worked with RFID systems—whether it’s for access control, inventory tracking, or animal tagging—you’ve probably heard the term RFID programmer tossed around. But what exactly does it do, and why is it so important in the RFID setup? Let’s break it down in plain English.
An RFID programmer is basically the “brain” that writes information onto RFID tags and sometimes reads it back. Think of it like a USB writer for smart tags. You connect it to your computer, open some software, and then assign data—like product IDs, asset numbers, or even livestock details—to the tag’s memory chip.
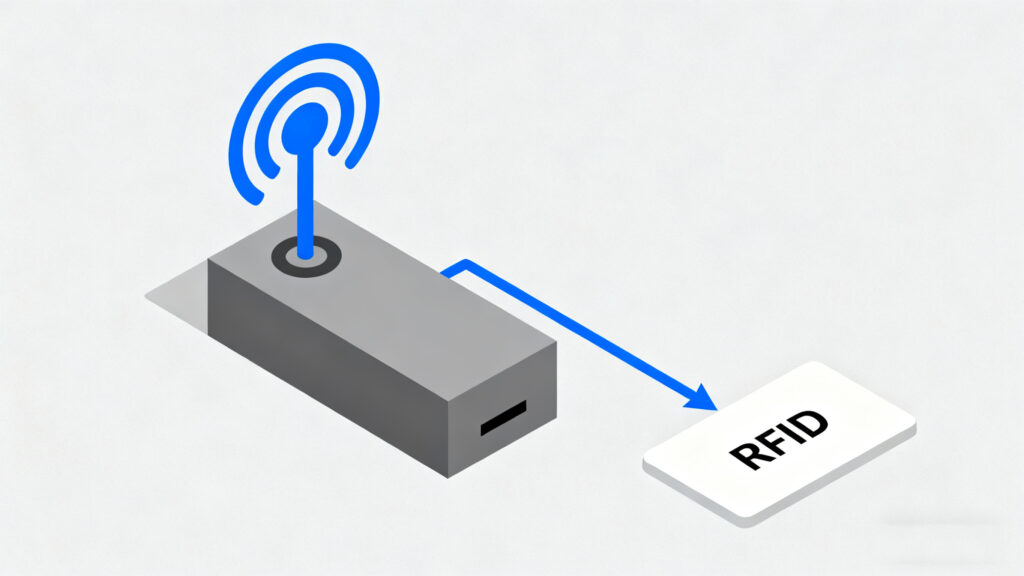
There are two main things it handles:
In short, it’s what makes a blank RFID tag useful and unique.
Programming an RFID tag usually happens through a UHF or HF reader/writer device. When you place the tag near the antenna, the programmer sends a signal that activates the chip. The software then encodes your chosen data into the tag’s memory area.
A typical setup includes:
Once programmed, these tags can be read by compatible readers in your warehouse, shop, or factory floor.
A nice thing about programming your own tags is that you control what data gets written. That means better accuracy, less confusion, and less dependency on pre-coded tags.
Depending on your project, you’ll run into different types of programmers:
Some models can even handle both reading and writing in one go, making them ideal for testing and verifying tag performance.
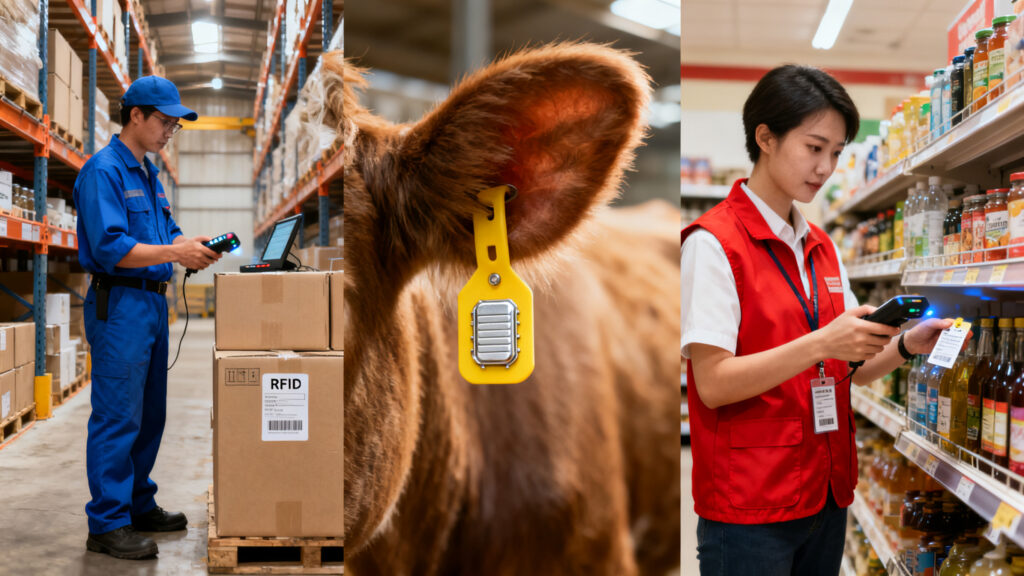

RFID programming plays a role in many industries:
Basically, anywhere you see RFID tags, there’s probably an RFID programmer somewhere in the workflow.
If you’re new to RFID programming, here are some practical tips:
An RFID programmer might sound technical, but once you see how it works, it’s actually pretty straightforward. It’s just the tool that gives your RFID system life—turning blank tags into meaningful data carriers that keep your workflow smart and efficient.
Whether you’re managing livestock, controlling factory inventory, or running a logistics operation, learning how to use an RFID programmer is one of those small steps that makes your system a lot more powerful.

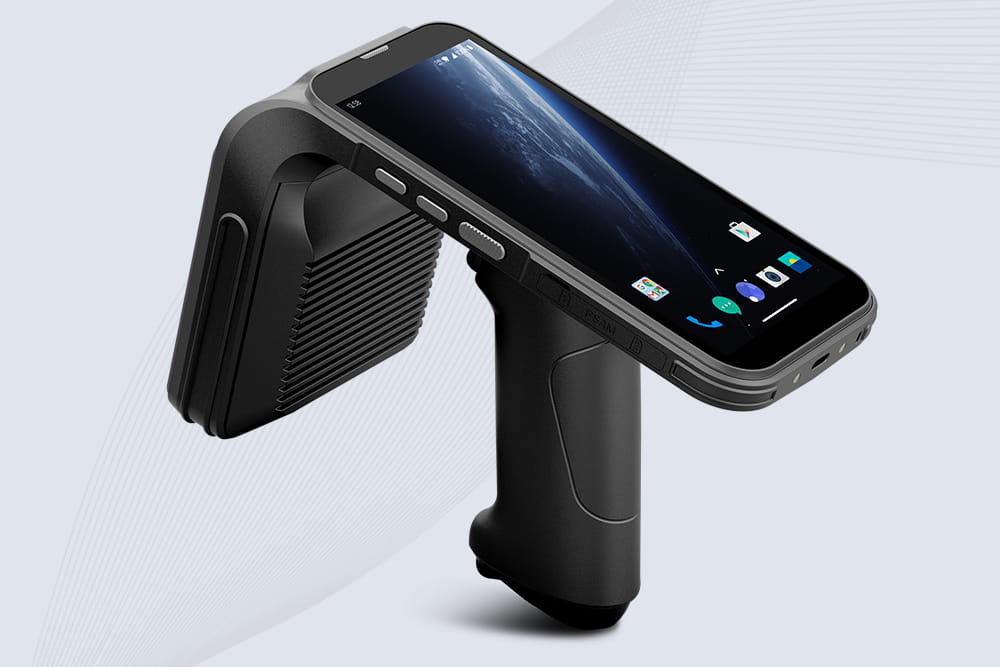
Cykeo CYKEO-B9 UHF Bluetooth handheld RFID scanner features 12m UHF range, 200+ tags/sec scanning, IP67 rugged design for retail/warehouse/pharma. Supports Android SDK & real-time Bluetooth 5.0 transmission.

Cykeo CYKEO-B4 UHF Handheld RFID Reader scanner delivers 1300 tags/sec reading, 30m UHF range, and 12-hour battery life. IP65 rugged design with barcode/NFC/ID scanning for retail/manufacturing/logistics.
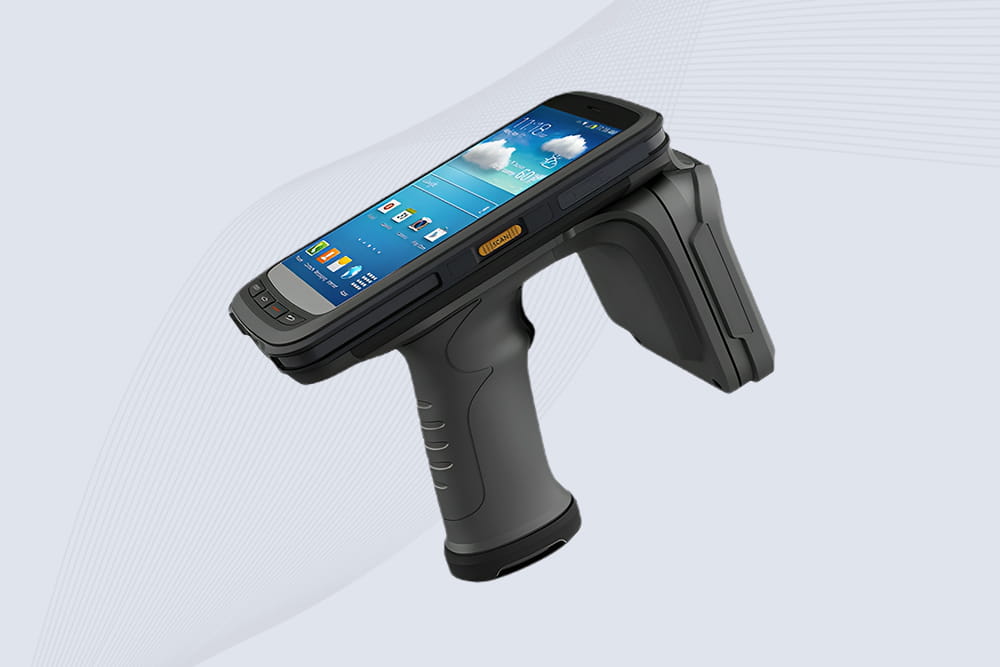

Cykeo CYKEO-B2 industrial UHF RFID handheld offers 10m range, 500 tags/sec scanning, Android 11 OS, and IP65 rugged design for retail/warehouse/manufacturing.
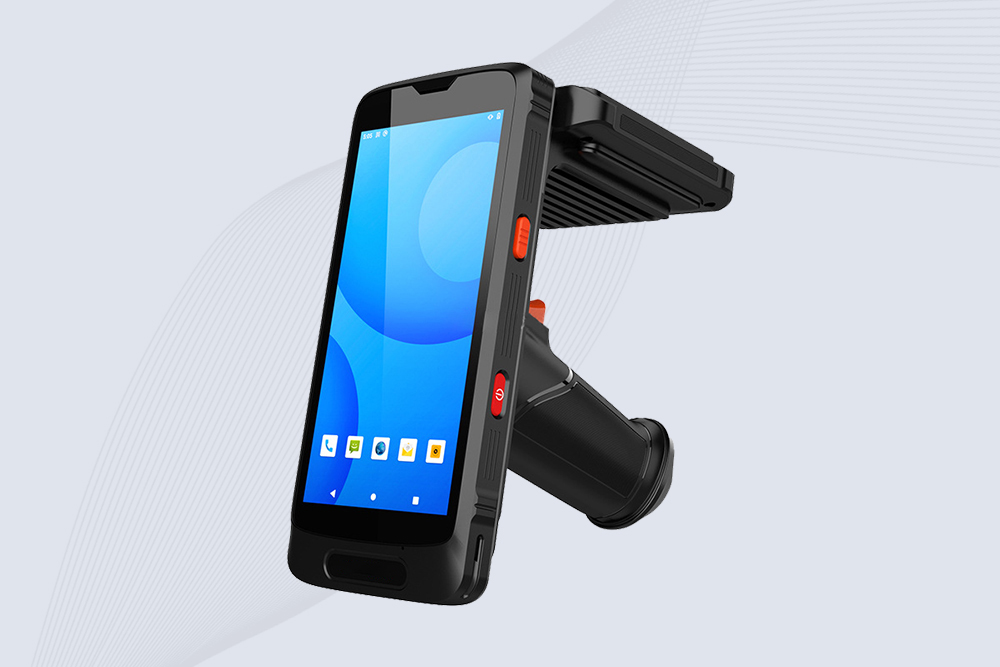

Cykeo CYKEO-B3 industrial RFID Reader Handheld, terminal offers 2m read range, multi-protocol scanning (NFC/barcode/ID), Android 10 OS, and IP65 ruggedness for logistics/retail/manufacturing.
Discover the hidden costs of handheld RFID scanners—hardware, software, maintenance, and more. Learn how to calculate ROI and avoid budget surprises.
MoreLearn what is an RFID card reader, how it works for security, payments, and attendance. Discover CYKEO's reliable RFID card reader solutions.
Morehow exactly is RFID applied to inventory management? And what unique advantages does it offer?
MoreRFID systems are rapidly replacing traditional barcode-based inventory control. This article explores five key applications of RFID in warehouse and logistics management, helping wholesalers and enterprises achieve efficient, low-error operations.
More