How to Test RFID Tags with Your Smartphone (No Scanner Needed)
1298Learn how to test RFID tags using your smartphone’s NFC feature. Discover apps, DIY methods, and troubleshooting tips for quick verification.
MoreAll RFID Product
If you’ve ever worked on a cattle farm, you know how chaotic it can get — hundreds of cows moving around, feeding, breeding, and sometimes wandering off. Keeping track of every animal’s health, location, and productivity manually is a nightmare. That’s where RFID cow tags come in.
These little electronic tags have become one of the most practical tools for modern livestock management. Let’s break down how they work, what types exist, and why they’re such a game changer in the field.
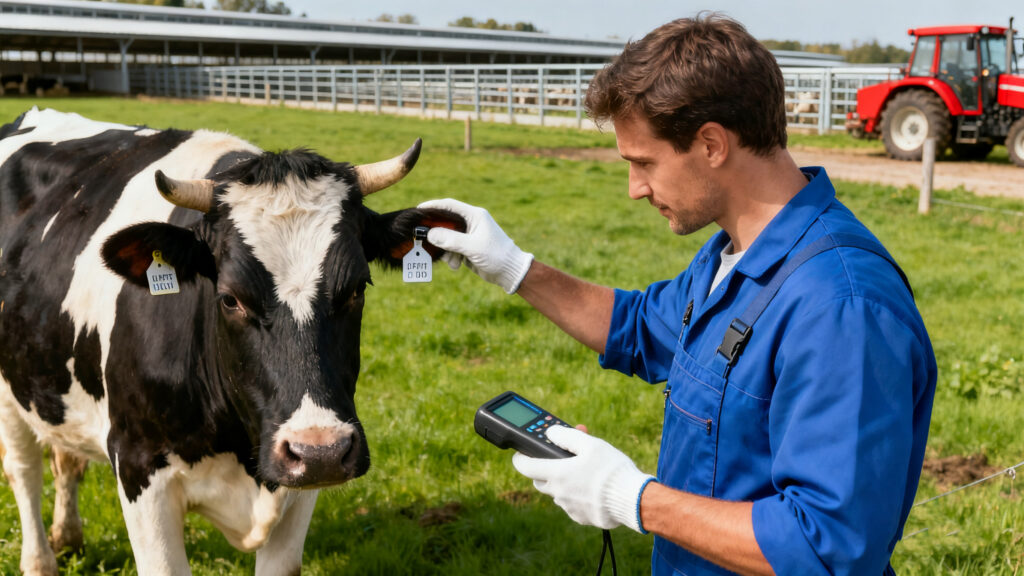

RFID stands for Radio Frequency Identification. In simple terms, it’s a system that uses radio waves to identify and track objects — in this case, cows.
Each RFID cow tag has a small microchip and an antenna sealed inside a durable housing. When a reader sends out a signal, the tag responds with its unique ID. That ID connects to data in the farm’s management software — things like age, vaccination history, milk production, and more.
The best part? You don’t need to physically catch the animal or even see the tag. The reader can scan it from several meters away, saving hours of manual labor.
Most farms use RFID tags for three main reasons:
There are a few types depending on how they’re used:
Each tag type works differently depending on how rugged you need it to be, how far you want to scan, and whether you’re tracking health data or just identification.
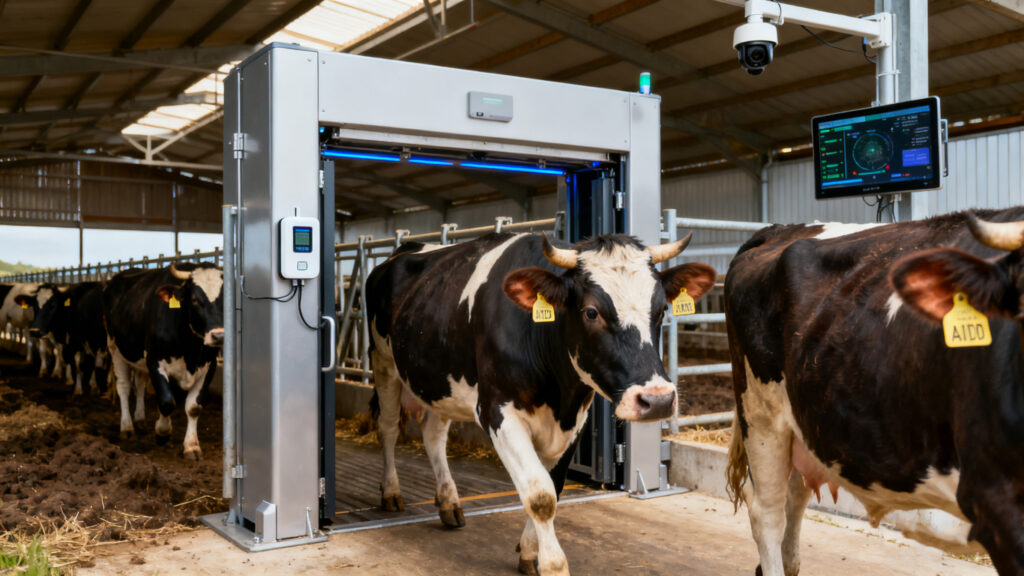

The system usually includes three parts:
When a cow walks past a reader, the tag transmits its unique ID number. That number instantly pulls up the cow’s data in the system — feed schedule, health records, breeding dates, you name it.
Over time, this data helps farmers make smarter decisions — which cows are producing well, which need attention, and how to optimize the herd overall.
RFID tagging isn’t perfect. Tags can get damaged or lost, especially in rough environments. Readers and software systems also require some investment and training. But compared to the long-term savings and efficiency, most farmers say it’s worth it.
As farming gets smarter, RFID cow tags are becoming part of a bigger picture — integrated data systems, automated feeding, and precision livestock farming. They’re not just about ID numbers anymore; they’re part of how farms are staying profitable and sustainable in a changing world.
So next time you see a cow with a small plastic tag on its ear, remember — that little chip is helping farmers manage an entire herd smarter and faster than ever before.
CYKEO Passive RFID Tags are made for wet and high-humidity environments where standard labels do not last. This rfid passive tag is often used around liquids, chemicals and temperature changes, providing stable reading distance and long data life for industrial tracking.
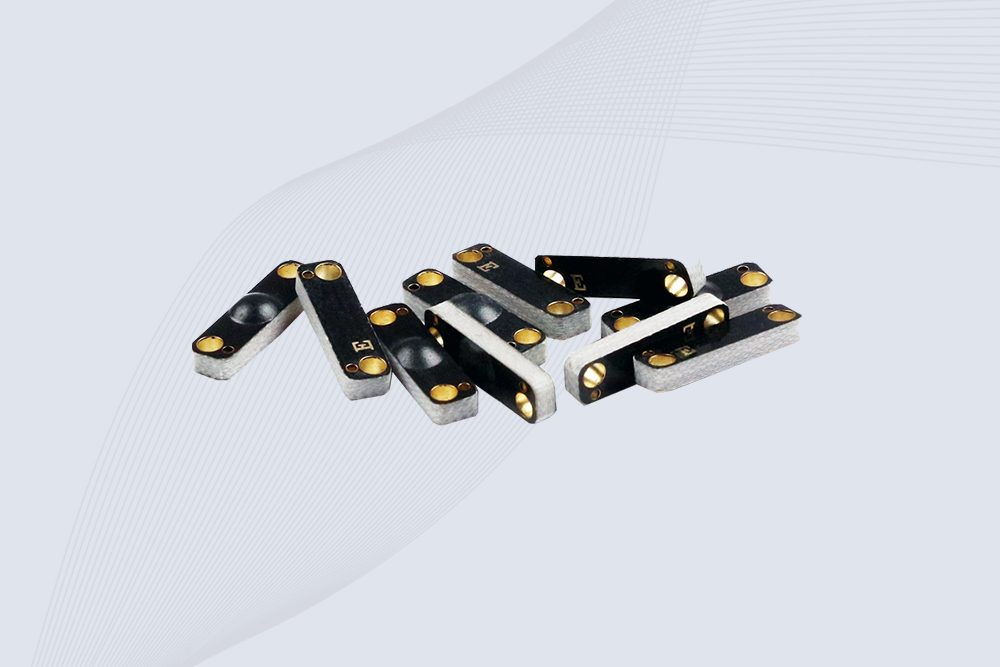

CYKEO CK-BQ1504 Metal RFID Tags is a compact anti-metal UHF RFID solution built for direct mounting on metal surfaces. With stable 8-meter read range, Ucode-8 chip, and long data retention, this rfid metal tag fits tools, containers, automotive parts, and industrial asset tracking.
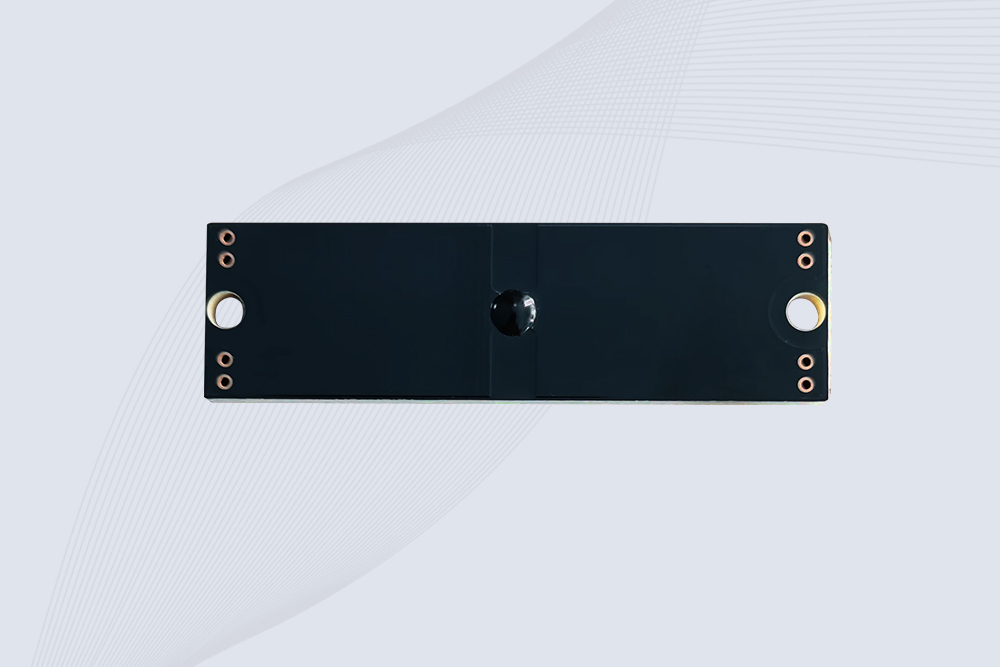

CYKEO CK-BQ7020 On-Metal RFID Tags are designed for reliable tracking on steel and metal surfaces. Built with an FR4 epoxy body and industrial-grade chips, these On-Metal RFID Tags deliver stable performance, long data life, and chemical resistance, making them a dependable RFID anti-metal tag for harsh environments.
The CYKEO CK-BQ6025 Anti-Metal RFID Tag is built for metal surfaces where standard tags fail. Designed for long-range performance, harsh environments, and stable data retention, this Anti-Metal RFID Tag is ideal for industrial assets, containers, and equipment tracking using on metal RFID tags.
Learn how to test RFID tags using your smartphone’s NFC feature. Discover apps, DIY methods, and troubleshooting tips for quick verification.
MoreConfused? We clarify if an RFID antenna and reader are two separate devices, explaining integrated vs. external setups for different applications.
MoreA detailed look at the CK-M8 UHF RFID 8-port module, its features, real-world performance, specs, and how it compares to Impinj R2000-based modules. Suitable for warehouses, logistics, manufacturing, and retail tracking systems.
MoreExplore the technical structure of a hospital parking system using RFID, including reader modules, antennas, and how Cykeo RFID hardware integrates into complex hospital environments.
More