Whatever Happened to RFID?
679Discover how RFID has evolved from early hype to a critical tool in industries like retail, healthcare, and IoT. Learn how Cykeo’s solutions keep RFID relevant today.
MoreAll RFID Product
Handheld RFID reader is portable wireless device capable of reading RFID tags, displaying data in real time, and managing information. Compared with fixed readers, it offers greater flexibility and convenience for mobile operations. These devices are widely applied in:
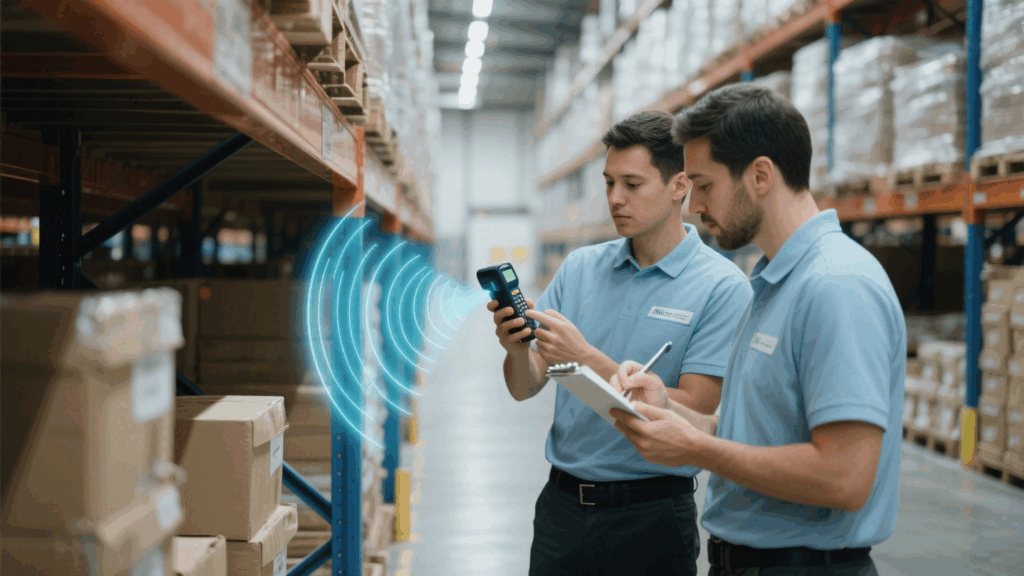

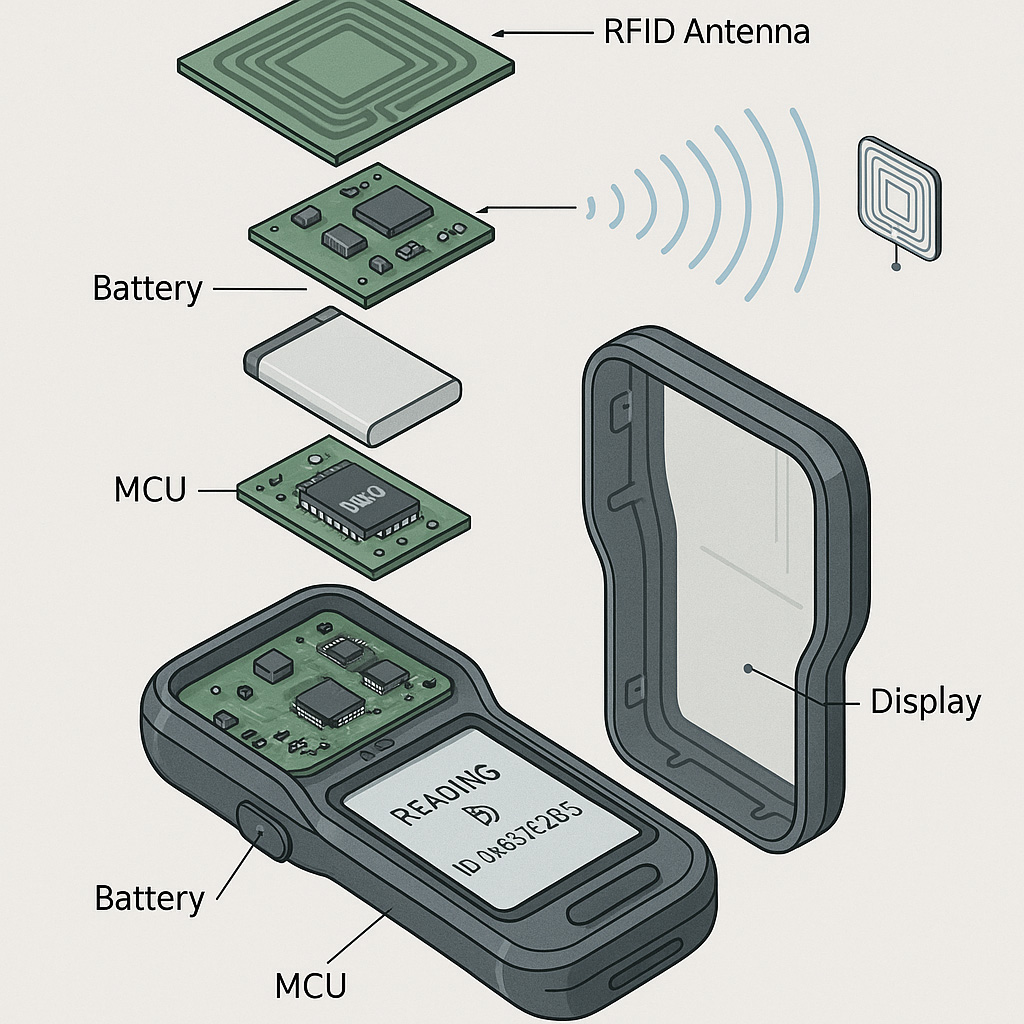
A handheld RFID reader typically integrates an RFID module, antenna, display control system, and communication modules, forming a standalone terminal. The typical workflow is as follows:
Depending on the model, devices may run Android or Windows Embedded OS, supporting custom app installations and local data storage. Some also integrate barcode/QR code scanners to enable multi-function recognition within one device.
Based on application scenarios and reading distance needs, handheld RFID devices mainly support three frequency bands:
| Frequency Band | Operating Frequency | Characteristics | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| LF (Low Frequency) | 125 / 134.2 kHz | Short reading distance, good anti-interference | Animal identification, access control |
| HF (High Frequency) | 13.56 MHz | Medium reading distance, globally compatible | Libraries, medical equipment management |
| UHF (Ultra High Frequency) | 860–960 MHz | Long reading distance, supports multi-tag reading | Industrial inventory, warehouse logistics |
Most UHF handheld readers support international standards such as EPC Gen2 (ISO 18000-6C), ensuring compatibility with mainstream tags worldwide and enhancing cross-system deployment. Additionally, devices often allow flexible antenna power adjustment to adapt to both long- and short-distance recognition scenarios.
Choosing the right handheld RFID reader requires considering the specific application environment, budget, and technical parameters. Key factors include:
Due to its flexibility and mobility, handheld RFID readers demonstrate high practical value across various industries. Typical cases include:
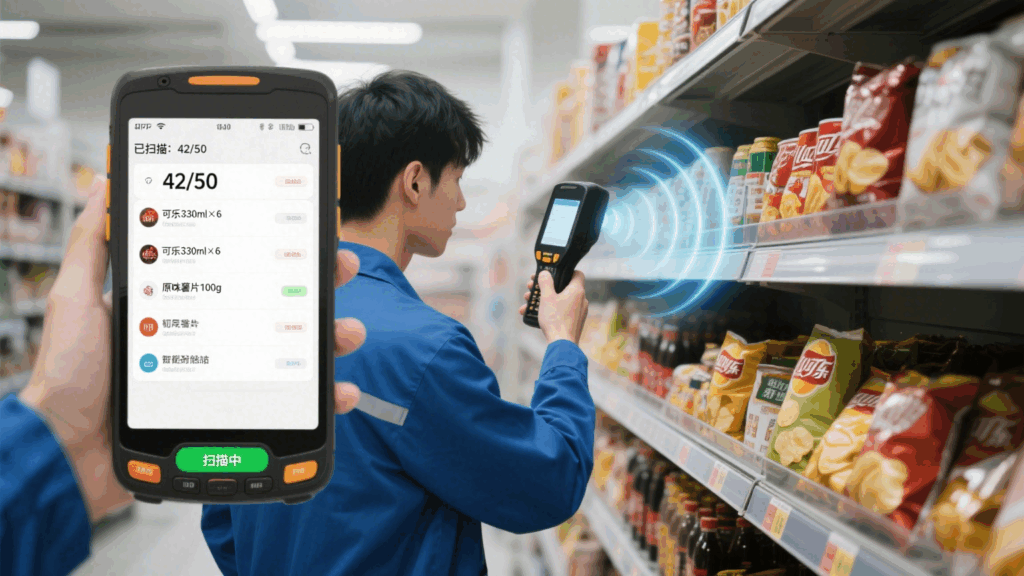

As key tool for automated asset tracking and data collection, handheld RFID readers have excelled in industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, and retail. When purchasing, prioritize:
For enterprises in the early stages of digital transformation, it is recommended to select general-purpose UHF handheld terminals and gradually build an RFID-based intelligent tracking and management system.
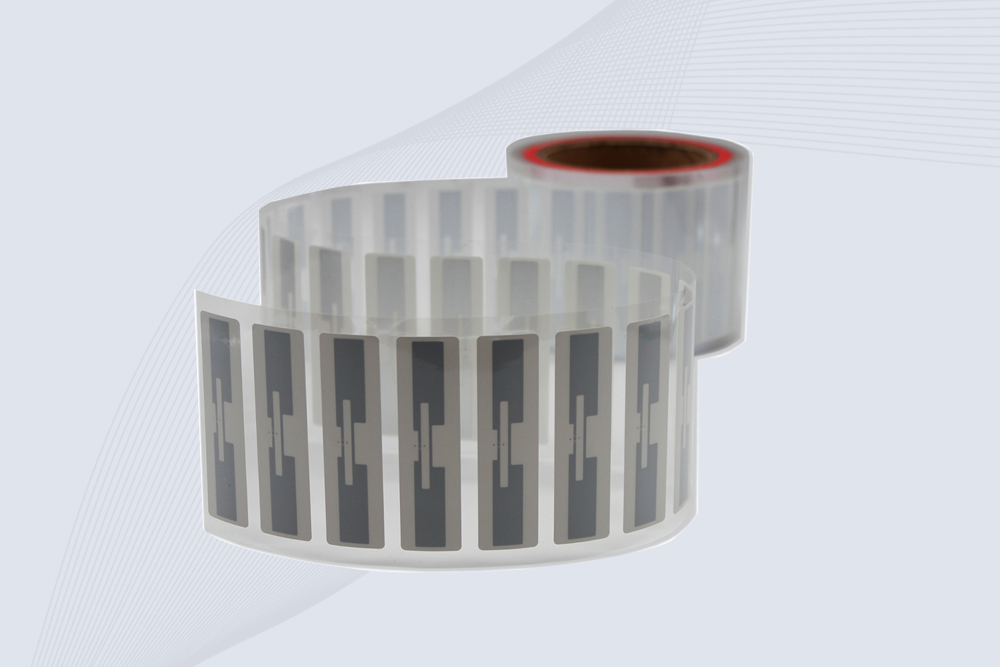
CYKEO Passive RFID Tags are made for wet and high-humidity environments where standard labels do not last. This rfid passive tag is often used around liquids, chemicals and temperature changes, providing stable reading distance and long data life for industrial tracking.
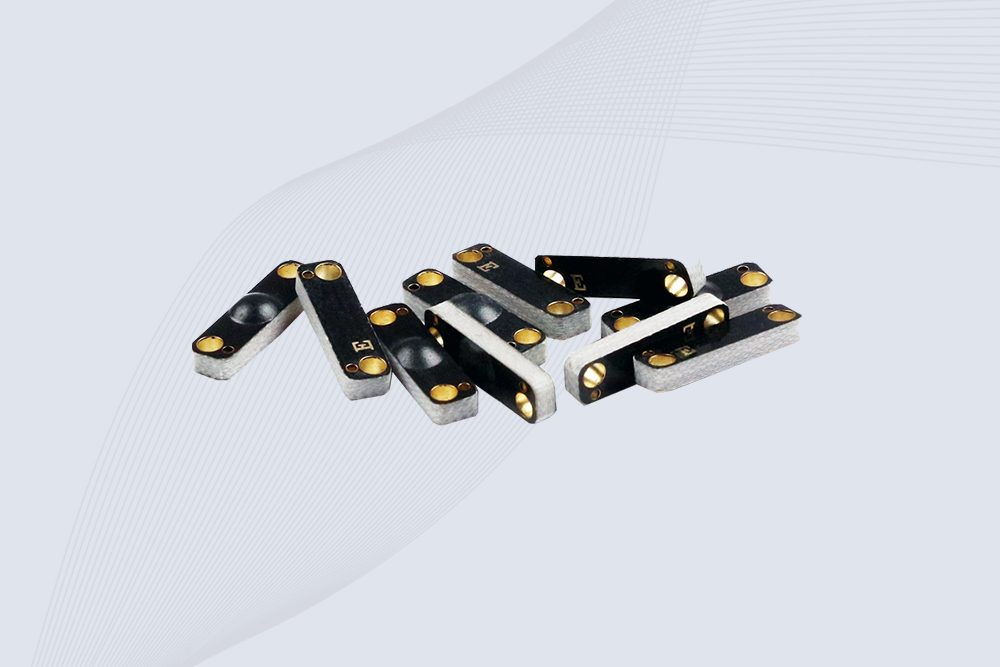

CYKEO CK-BQ1504 Metal RFID Tags is a compact anti-metal UHF RFID solution built for direct mounting on metal surfaces. With stable 8-meter read range, Ucode-8 chip, and long data retention, this rfid metal tag fits tools, containers, automotive parts, and industrial asset tracking.
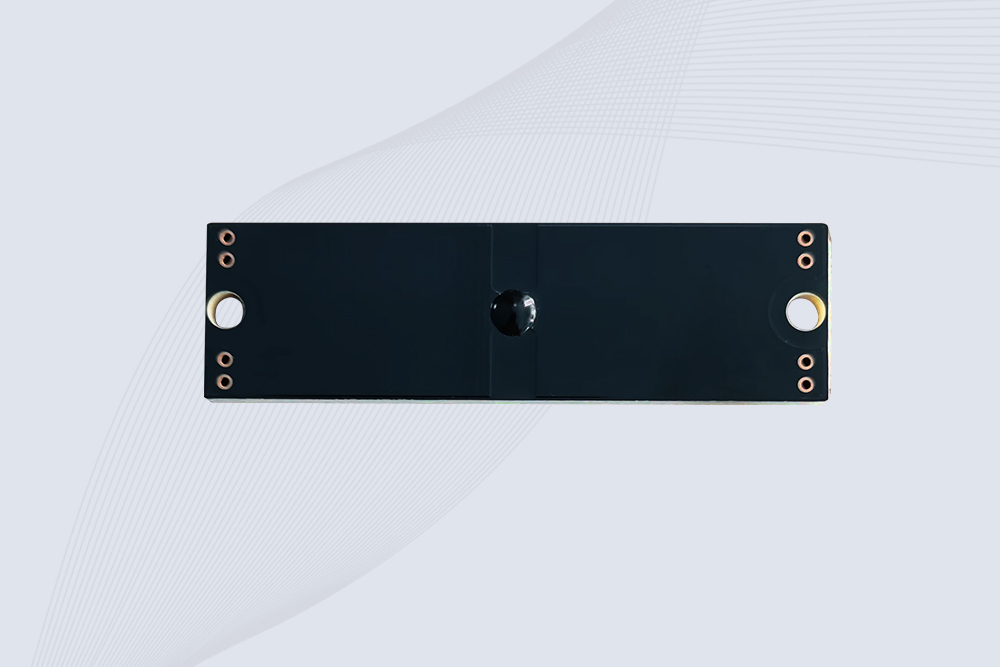

CYKEO CK-BQ7020 On-Metal RFID Tags are designed for reliable tracking on steel and metal surfaces. Built with an FR4 epoxy body and industrial-grade chips, these On-Metal RFID Tags deliver stable performance, long data life, and chemical resistance, making them a dependable RFID anti-metal tag for harsh environments.
The CYKEO CK-BQ6025 Anti-Metal RFID Tag is built for metal surfaces where standard tags fail. Designed for long-range performance, harsh environments, and stable data retention, this Anti-Metal RFID Tag is ideal for industrial assets, containers, and equipment tracking using on metal RFID tags.
Discover how RFID has evolved from early hype to a critical tool in industries like retail, healthcare, and IoT. Learn how Cykeo’s solutions keep RFID relevant today.
MoreNeed a tiny tracking solution? Learn how small an RFID antenna can be, the technology behind miniaturization, and the trade-offs between size and performance.
MoreEnsure secure, FDA-compliant controlled substance management with the FTNG‑L‑CK‑03 RFID Pharmacy Security Cabinet. Ideal for hospital pharmacies, addiction clinics, emergency departments, and research labs. Supports API integration, SDK for custom...
MoreInventory RFID tags, with features such as contactless identification, batch reading, and strong anti-interference capabilities, have become a standard technology in enterprise digital transformation.
More