How to Troubleshoot Read Errors in Long-Range RFID Systems?
479Struggling with read errors in your long-range RFID system? Learn step-by-step fixes for interference, tag placement, and hardware issues using Cykeo’s proven strategies.
MoreAll RFID Product
Chipless RFID is a type of radio-frequency identification technology that operates without the use of integrated circuit chips. Unlike conventional RFID systems, chipless RFID relies on specific material structures such as conductive ink, metal resonators, or resonant units to store and transmit information. By eliminating the chip, the tags become thinner, more flexible, and can even be directly printed onto paper or packaging materials.
Its reading mechanism is based on the concept of “reflected signatures.” A reader emits a radio signal, which the tag reflects in a unique spectral pattern that can be recognized and decoded. This approach not only reduces costs but also provides greater application flexibility.

The core of chipless RFID lies in how information is encoded. There are two main encoding strategies:
This method uses multiple resonators, each with a different resonant frequency. Each resonance peak represents a bit of data — for example, a response at a frequency indicates a “1,” and no response indicates a “0.”
This technique uses transmission lines of different lengths or delay structures. The reflected signals produce distinct echoes on the time axis, which encode the data.
Additionally, hybrid encoding techniques (such as frequency + polarization modulation) are being explored to improve data density.
Chipless RFID is being adopted across a growing number of real-world scenarios:
Chipless RFID remains in rapid development, with the following future directions:
Green Manufacturing: Advancement of printed electronics and biodegradable materials for sustainable production
Higher Encoding Density: Research into smaller resonators and higher frequencies to store more data
Flexible Material Innovation: Development of stretchable, bendable tag materials for wearables and textile integration
Sensor Integration: Combining RFID tags with embedded sensors for “read-and-sense” capabilities
AI-Assisted Decoding: Leveraging machine learning to improve multi-tag recognition and error correction
With its low cost, eco-friendliness, and scalability, chipless RFID is emerging as a key technology for smart labeling and IoT tracking systems. Although current limitations exist in terms of data capacity and reading accuracy, ongoing progress in material science and decoding algorithms is expected to expand its practical applications.
As businesses look to adopt these novel identification technologies, early adopters of chipless RFID stand to reduce IoT deployment costs significantly, gain differentiated advantages, and move toward a more intelligent and efficient digital future.
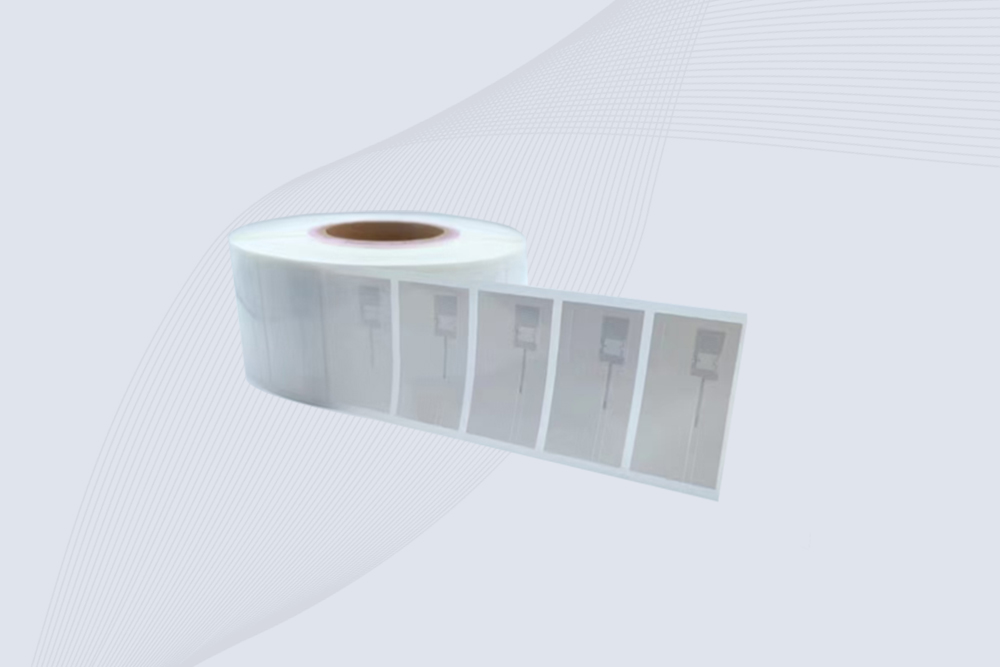

Cykeo CK-BQ6826 Jewelry uhf rfid tag features NXP UCODE 9, 8m read range on metal, and anti-counterfeit security for luxury assets.
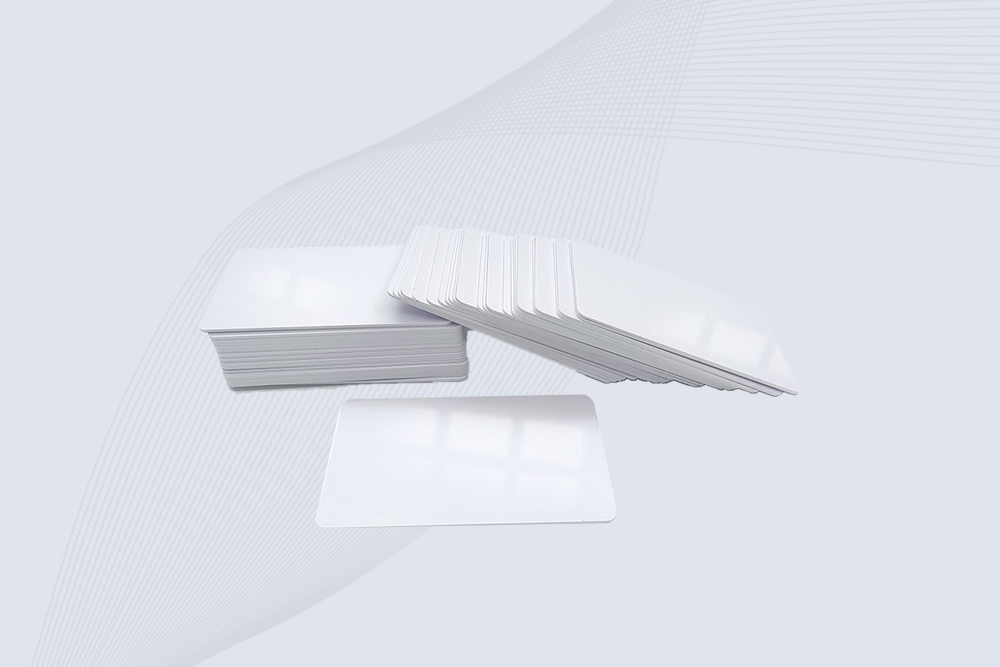

Cykeo CK-BQ8554HF HF rfid cards feature FM1108 chip, 100K write cycles, and customizable printing for access control systems.

Cykeo CK-BQ8554UHF uhf rfid card features U9 chip, 100K write cycles, and CR80 size for access control/inventory management.

Cykeo CK-BQ7320 UHF RFID asset tag features aluminum-etched antenna, 10-year data retention, and -40°C to +85°C operation for industrial tracking. ISO/IEC 18000-6C compliant with 128-bit EPC memory.
Struggling with read errors in your long-range RFID system? Learn step-by-step fixes for interference, tag placement, and hardware issues using Cykeo’s proven strategies.
MoreProtect your fixed RFID readers from cyber threats with Cykeo’s expert strategies. Learn encryption, network hardening, and compliance practices to safeguard sensitive data.
MoreLearn how to obtain data from RFID tags via Bluetooth for seamless wireless workflows. Discover compatible devices, setup steps, and Cykeo’s Bluetooth-enabled RFID solutions.
MoreKeep your RFID data safe! Learn proven methods to secure wireless RFID modules from eavesdropping, cloning, and unauthorized access.
More