RFID in Manufacturing: What I’ve Learned
60Discover how RFID technology really works in manufacturing. Real-world experiences, practical tips, and lessons learned from implementing RFID systems for inventory, production, and quality control.
MoreAll RFID Product
RFID technology has revolutionized industries by automating data collection, but choosing between passive RFID tags and active RFID systems can be daunting. Whether you’re managing a warehouse, tracking medical equipment, or optimizing supply chains, understanding their strengths and limitations is key to maximizing ROI. Let’s dive into what sets them apart—and how to pick the right fit.

Passive RFID Tags
Active RFID Systems
1. Tracking Range and Environment
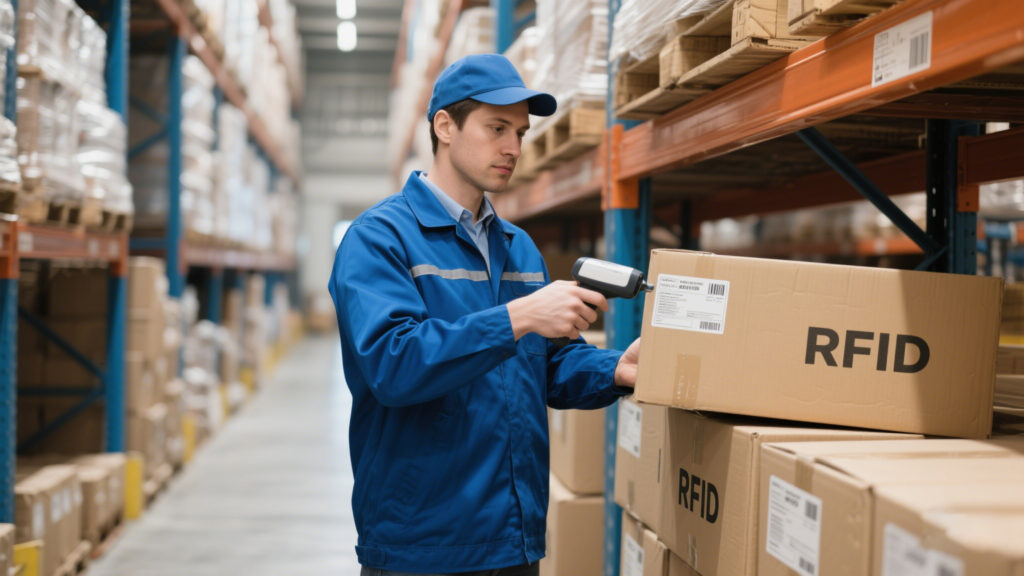

2. Budget and Scalability
3. Data Frequency and Functionality
Passive RFID Use Cases
Active RFID Use Cases
Cykeo offers hybrid RFID readers that support both passive and active tag protocols, ideal for businesses transitioning between systems. For instance, a warehouse storing bulk goods (passive-tagged) and high-value machinery (active-tagged) can use a single Cykeo reader to manage both, reducing hardware costs by 30%.
1. Interference Issues
2. Battery Life in Active Systems
3. Scalability
Semi-passive RFID tags are gaining traction. These battery-assisted tags use power only for sensors (e.g., temperature logging) while relying on reader energy for communication. They’re perfect for pharmaceutical logistics, where real-time environmental data is critical.
Discover how RFID technology really works in manufacturing. Real-world experiences, practical tips, and lessons learned from implementing RFID systems for inventory, production, and quality control.
MoreLooking to buy a UHF RFID four-port fixed reader? Learn how to choose the right model, understand key specs, and build a reliable RFID solution for logistics, automation, or access control.
MoreStruggling with HF RFID interference in your library? Learn how to reduce signal issues, improve scan accuracy, and keep your inventory system running smoothly.
MoreRFID vs GPS: Discover key differences in range, cost & accuracy. Learn when to use each for assets, vehicles, or inventory. Make informed decisions.
More