Can Smartphones Read RFID? Let’s Get Real.
39Wondering if you can use smartphones to read RFID? We explain the NFC capability, its severe limitations, and when you need professional RFID hardware.
MoreAll RFID Product
As vital part of the Internet of Things (IoT), RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology is being widely adopted across various industries. Understanding what RFID is and how RFID works not only helps you stay ahead of industry trends but also opens the door to new business opportunities. In this guide, we’ll dive into the fundamentals of RFID—its definition, how it works, its core components, application scenarios, and key benefits—to demystify this transformative technology.
RFID, short for Radio Frequency Identification, is technology that uses radio waves and spatial coupling (via alternating magnetic or electromagnetic fields) to transmit data wirelessly for identification purposes. A complete RFID system consists of three main components: electronic tags (also known as RFID tags), readers, and antennas.
RFID Tags: These contain a coupling element and a chip. Each tag carries a unique electronic code—acting like “digital ID card” for an object—and stores data such as item name, model, and production date. Based on power source, tags are classified as:
Active tags (with built-in batteries that actively transmit signals),
Passive tags (which rely on energy from the reader’s electromagnetic field), and
Semi-active tags (with battery but activated by reader’s signal).
RFID Reader: This device reads or writes data to RFID tags. It communicates with tags by emitting radio signals via antenna and sends the collected data to the backend system for processing.
Antenna: It transmits and receives radio signals between the reader and the tag. Its design and performance directly affect the system’s read range and overall reliability.
Because its advantages of contactless identification, batch processing, and fast recognition speed, RFID technology finds broad applications across many industries:
Logistics and Supply Chain Management: Enables real-time tracking, rapid inventory counting, and automated sorting of goods, significantly boosting logistics efficiency.
Retail: Supports theft prevention, inventory management, and self-checkout systems, enhancing the shopping experience and operational productivity.
Transportation: Applied in toll collection systems like highway ETC and vehicle identification to speed up traffic flow.
Healthcare: Used for patient identification, drug traceability, and medical equipment management, ensuring safety in medical operations.
Asset Management: Helps enterprises efficiently manage fixed assets by enabling quick location tracking and inventory audits.

High Efficiency: RFID can simultaneously identify multiple tags, enabling batch processing and significantly improving efficiency compared to traditional barcode scanning.
Accuracy: RFID readings are highly accurate and unaffected by environmental factors such as dust, dirt, or lighting conditions.
Long-Range Identification: Some high-performance RFID systems can read tags from several meters or even tens of meters away.
Large Data Storage: Tags can store rich information and support repeated reading and writing of data.
Durability: RFID tags often feature waterproof, anti-magnetic, and high-temperature-resistant properties, ensuring a long service life.
For international trade customers, the following points are crucial when selecting RFID products:
Operating Frequency: Different RFID frequencies suit different scenarios:
Low Frequency (LF): Suitable for short-range, low-speed applications.
High Frequency (HF): Commonly used for access control and library management.
Ultra High Frequency (UHF): Ideal for long-distance, high-speed identification like logistics and warehousing.
Reading Distance: Choose the appropriate reading range based on actual use to avoid performance issues due to insufficient range.
Compatibility: Ensure the RFID products integrate seamlessly with existing systems such as ERP or WMS.
Supplier Credentials: Select suppliers with rich experience, strong reputation, and comprehensive after-sales service to guarantee product quality and ongoing support.
With the continuous development of IoT technologies, RFID’s application prospects are expanding rapidly. If you have procurement needs or technical inquiries about RFID products, feel free to contact us. We offer professional solutions and high-quality product services!
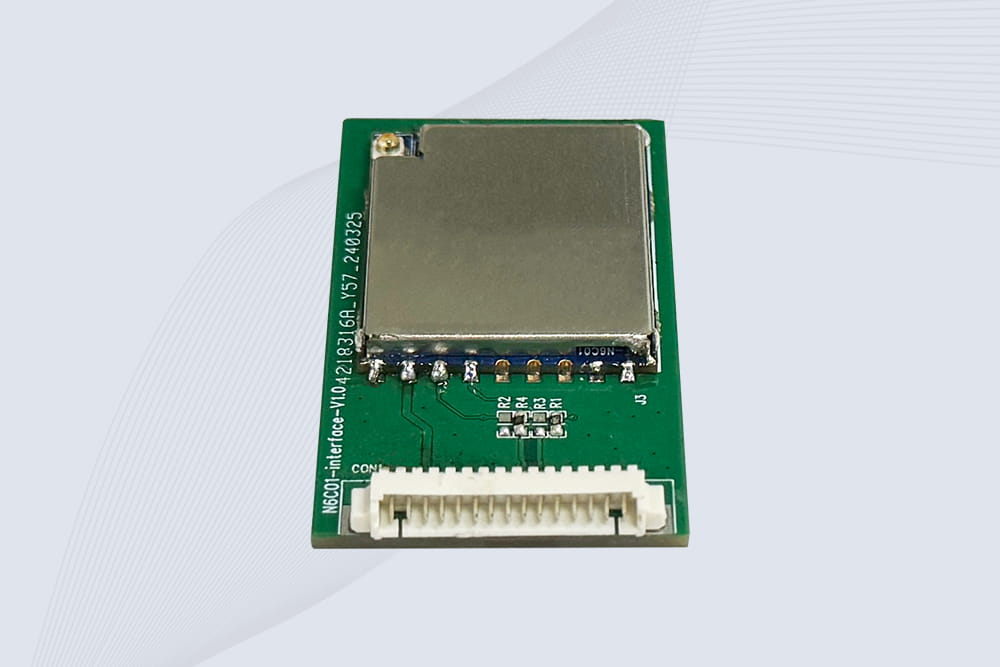

CYKEO Embedded RFID Modules are designed for compact industrial and IoT devices that require stable UHF performance. These UHF RFID Modules support global protocols, flexible power control, and reliable multi-tag reading for smart cabinets, production lines, and asset tracking systems.
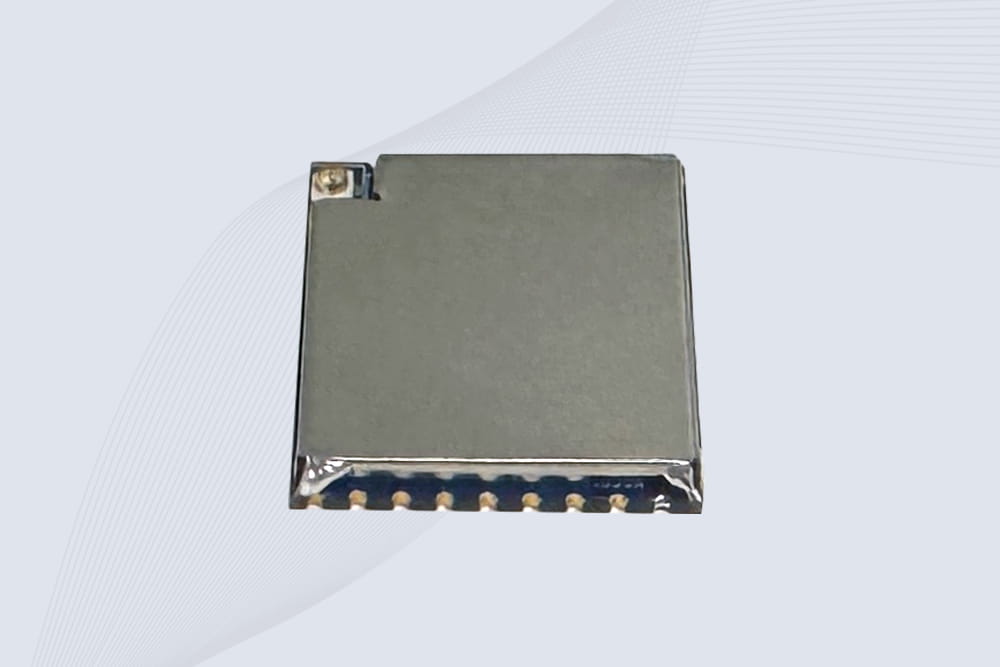

CYKEO Embedded RFID Module is built for compact IoT and industrial devices that need stable UHF performance. This UHF module supports global protocols, low power operation, and reliable multi-tag reading for smart lockers, production lines, and always-on RFID systems.
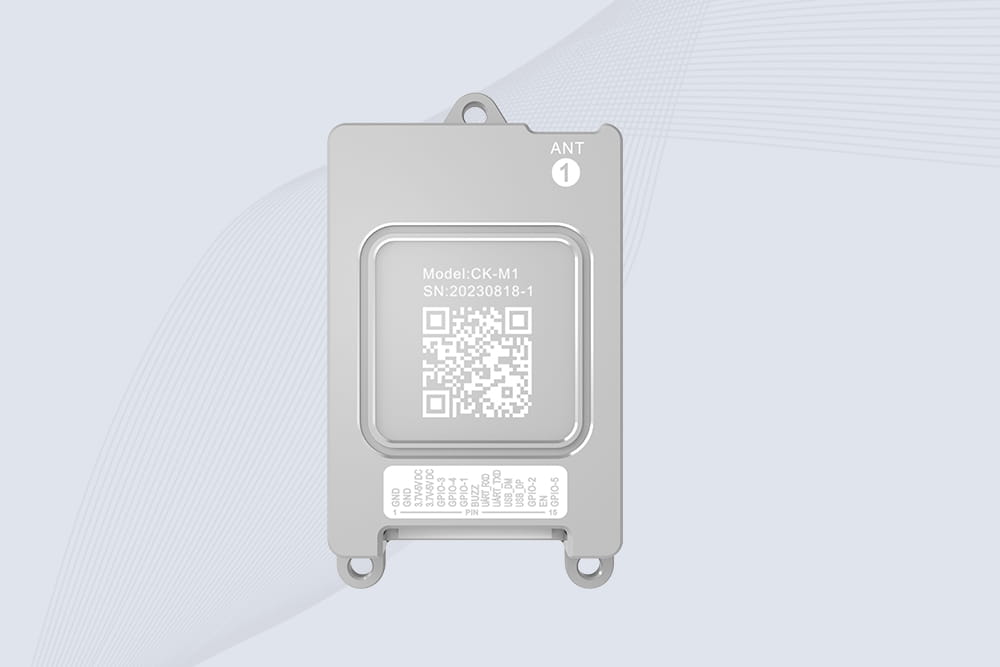

CYKEO CK-M1 drone rfid module is a compact UHF RFID reader module designed for drones and UAV platforms. It supports long-range aerial scanning, fast multi-tag reading, and stable performance in wind, vibration, and outdoor environments.
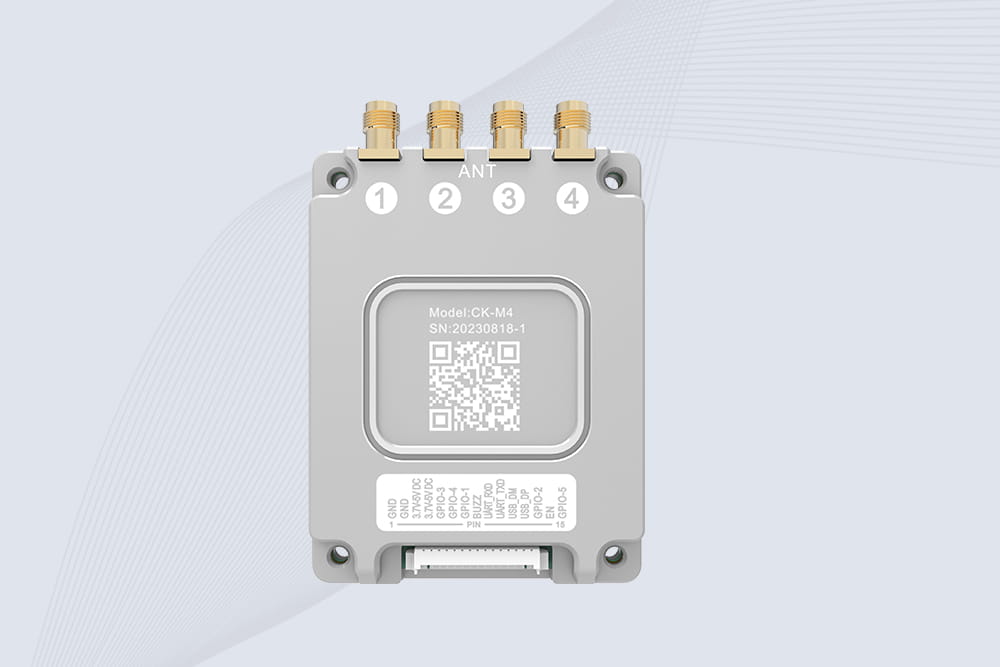

CYKEO CK-M4 RC522 RFID Module is an industrial-grade UHF RFID reader with 4 ports, supporting ISO, EPC, and GB protocols. High-speed, accurate reading for IoT, automation, and warehouse applications.
Wondering if you can use smartphones to read RFID? We explain the NFC capability, its severe limitations, and when you need professional RFID hardware.
MoreStep-by-step guide to installing and configuring industrial RFID readers for maximum efficiency. Learn best practices and avoid common pitfalls with Cykeo’s expertise.
MoreRFID readers for boom barriers boost security and traffic efficiency in parking lots, factories, and gated communities. Learn real deployment cases, setup tricks, and key questions before installation.
MoreConfused by RFID components? Learn what an RFID module is, how it powers tags and reads data, and why it's the essential building block for access control and tracking systems.
More