When Should You Choose Active vs Passive RFID Tracking?
338Confused about active vs passive RFID? Compare range, cost, battery life, and ideal use cases to pick the right technology for your needs.
MoreAll RFID Product
RFID antenna is the key device that connects RFID reader with RFID tags. It emits and receives radio frequency signals to power passive tags and enable system communication. Antenna performance directly affects read range, angle, and system stability.
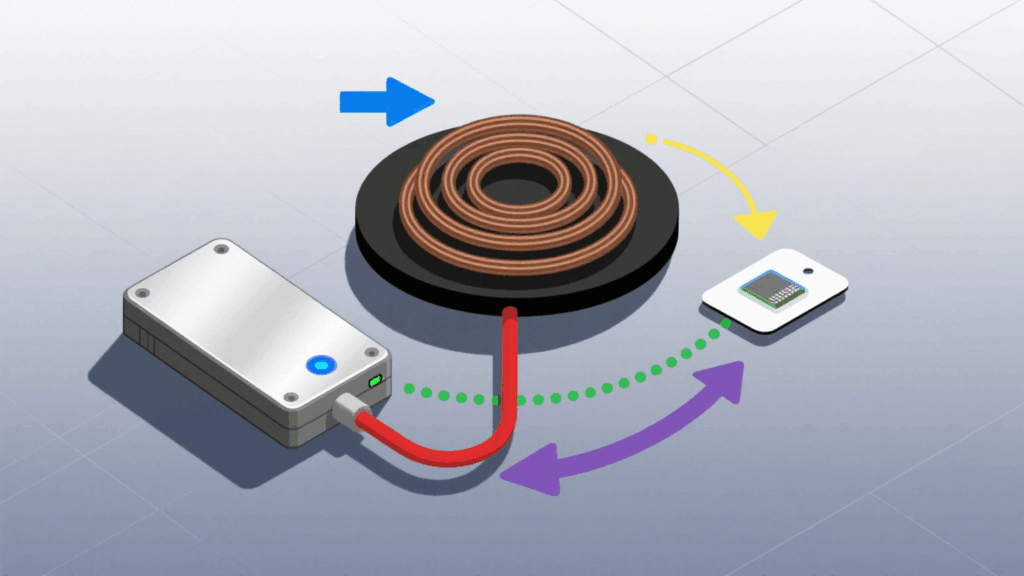
RFID antennas can be categorized based on frequency, structure, and installation environment:
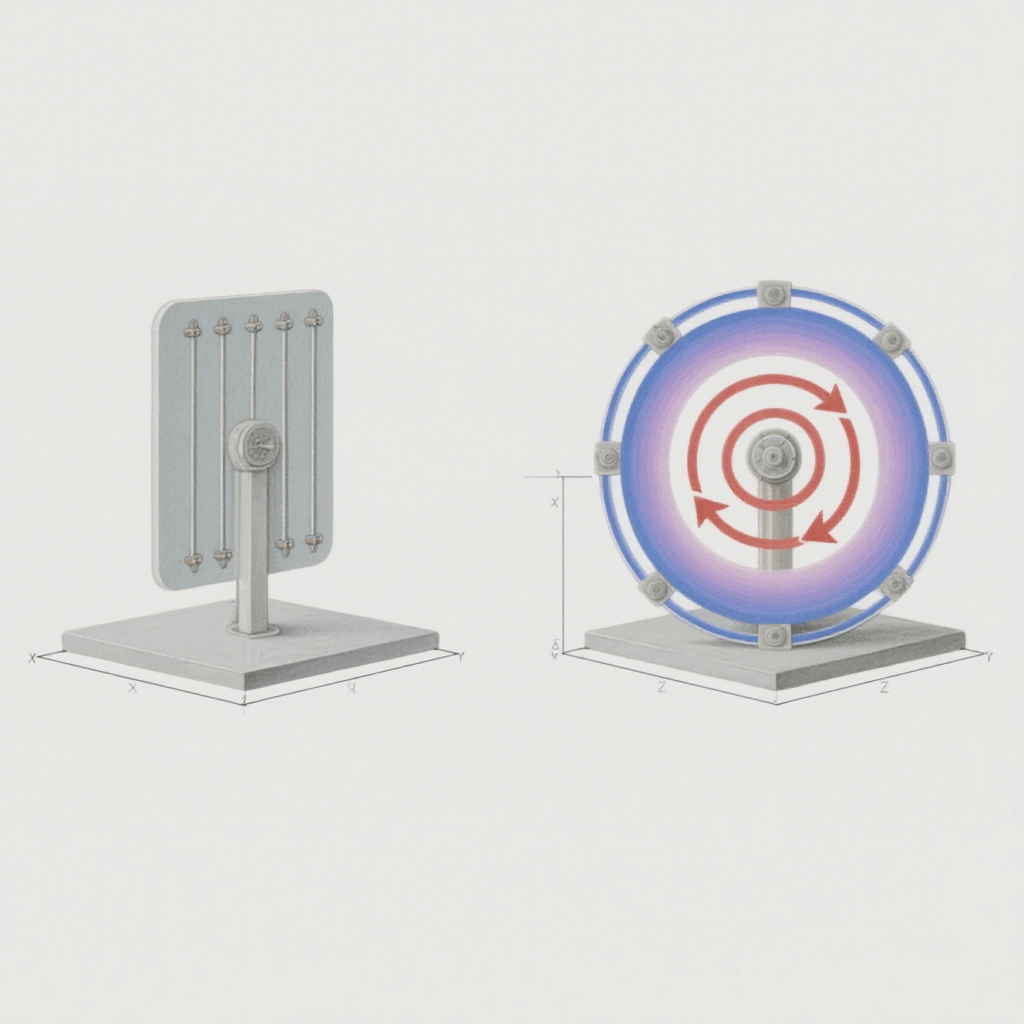
An antenna’s polarization determines the propagation direction of electromagnetic waves, which affects the tag recognition angle and range.
| Polarization Type | Features | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Linear | Strong directionality with long read range, but requires alignment with the tag’s orientation | Conveyor belts, directional read zones |
| Circular | Allows multi-angle reading with better adaptability, though read range is slightly shorter | Libraries, retail shelves, access control gates |
When selecting an RFID antenna, consider the following key factors:
Here are common examples of RFID antenna applications:

Cykeo CYKEO-A11 UHF RFID reader antenna delivers 11dBi gain, 840-960MHz frequency range, and IP65 ruggedness for retail, logistics, and industrial RFID systems. Features low VSWR and easy installation.

CYKEO Antenna RFID Reader delivers stable long-range UHF performance with a 10.5dBi directional design, built for warehouses, conveyor portals, and industrial RFID systems. This rfid reader antenna provides 20m+ read distance and rugged IP67 protection.

Cykeo CYKEO-PHF3 industrial HF RFID Antenna offers 24-point dynamic tracking, ISO 14443A/15693 protocols, metal-environment stability for archives/libraries/manufacturing.

Cykeo CYKEO-A5B industrial Linear RFID Antenna delivers 5dBi gain, ≤1.5:1 VSWR, and IP65 rugged design for warehouse, production line, and logistics UHF systems.
Confused about active vs passive RFID? Compare range, cost, battery life, and ideal use cases to pick the right technology for your needs.
MoreStep-by-step guide to installing and configuring industrial RFID readers for maximum efficiency. Learn best practices and avoid common pitfalls with Cykeo’s expertise.
MoreDiscover how RFID technology streamlines library processes like book lending, returns, and inventory management. Learn about automation, accuracy, and Cykeo’s library solutions.
MoreRewritable RFID tags for RFID software solution providers and developers
More