RFID Tester Market Size and Market Share Forecast (2025-2035)
42RFID tester market forecast from 2025 to 2035, covering market size, CAGR, applications, frequency bands, regional growth, and competitive landscape.
MoreAll RFID Product
According to research released by Future Market Insights, the global low-frequency (LF) RFID tag market is expected to expand from USD 1.4 billion in 2026 to USD 3.0 billion by 2036, representing a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.8%. Demand is concentrated in applications where reliable performance near metal or liquids is more critical than data rate or read distance, such as animal identification, access control, and industrial asset tracking. Adoption remains uneven, as many industries have shifted toward higher-frequency systems where operating conditions allow. Geographic cost advantages favor regions with large-scale embedded manufacturing and RFID antenna winding capabilities, particularly East Asia, which continues to influence global sourcing and pricing decisions.
System integrators and end users typically select LF RFID tags as part of closed-loop identification systems rather than as interchangeable components. Once tags are encoded into devices, livestock registries, or security systems, formats are rarely changed due to the costs associated with reprogramming and database migration. Certification requirements for animal tracking and access control systems further limit substitution. Smaller market segments continue to rely on LF RFID because of its environmental tolerance and compatibility with legacy systems. Overall market growth is driven by the gradual expansion of stable application segments and regulated identification programs, rather than by widespread replacement of other RFID standards.
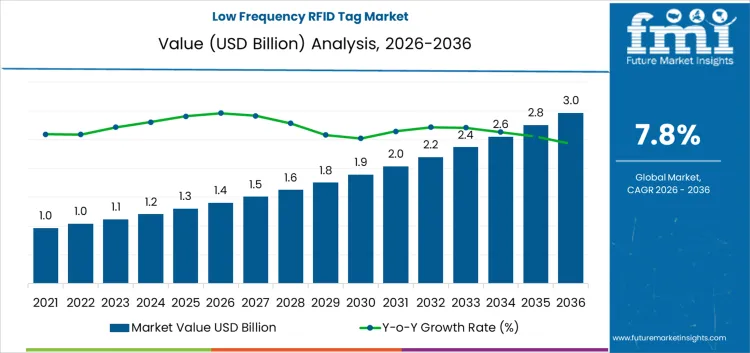
Growth in the LF RFID tag market occurs through gradual accumulation rather than step-change adoption. The market began at approximately USD 0.9 billion and expanded in close alignment with animal identification programs, access control deployments, and theft-prevention systems, rising incrementally to around USD 1.0–1.1 billion. Even as the market reaches USD 1.2 billion and subsequently USD 1.3 billion, momentum remains controlled, as expansion is driven by population growth and regulatory scale rather than by technology cycles.
The transition toward USD 1.4–1.5 billion reflects steady increases in the number of tagged livestock, pets, and secured assets rather than structural changes in usage. Pricing remains stable, with volume growth accounting for most revenue increases.
As the installed base grows, the market gradually reaches USD 1.6–1.8 billion, driven mainly by coverage expansion and system renewals rather than new use cases. Beyond USD 1.9 billion, entering the USD 2.1–2.3 billion range, replacement demand and regulatory programs begin to contribute volumes comparable to initial tagging. Subsequent growth to USD 2.5 billion, USD 2.7 billion, and ultimately USD 3.0 billion is driven by wider geographic rollout of the same core applications and higher tag density per herd, facility, or secured site. Throughout the forecast period, purchasing behavior remains conservative, with certification continuity and compatibility valued more than new functionality or higher data rates.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Market size (2026) | USD 1.4 billion |
| Forecast size (2036) | USD 3.0 billion |
| CAGR (2026–2036) | 7.8% |
Low-frequency RFID tags are increasingly used for reliable identification and tracking of assets, livestock, and access-controlled environments. Historically, identification relied on barcodes, magnetic stripes, or manual logs, which limited read distance, durability, and real-time visibility. Modern LF RFID tags operate at 125–134 kHz and deliver strong performance in environments with high metal content or moisture, enabling short-range, contactless reading.
Asset managers, logistics providers, livestock operators, and security administrators prioritize reliability, read accuracy, and compatibility with existing RFID readers. Early adoption focused on livestock tracking and access control, while current demand includes industrial inventory management, supply chain monitoring, and event access systems. These deployments are driven primarily by operational efficiency, security requirements, and regulatory compliance. Tag durability, read range, and environmental resistance influence supplier selection.
Operational efficiency, asset visibility, and security considerations continue to shape market growth. Compared with high-frequency and ultra-high-frequency RFID tags and optical identification solutions, LF RFID emphasizes robustness, low interference, and long-term reliability in complex environments. Cost structures depend on rfid tag materials, encoding methods, and durability, with margins concentrated among suppliers capable of delivering certified, high-performance RFID components. By 2036, LF RFID tags are expected to remain widely deployed across industrial, agricultural, and access control applications, supporting reliable identification and asset management in diverse environments.
In 2026, the LF RFID tag market is segmented by technology type and application. By technology, demand includes LF RFID proximity tags, read-only tags, read/write tags, and on-metal tags. Each is designed to meet specific memory requirements, mounting conditions, and read reliability challenges.
By application, demand spans animal identification, access control and security, supply chain and inventory management, and healthcare asset tracking. These segments differ in deployment scale, regulatory oversight, and tolerance for read errors. Collectively, they reflect user preference for reliability over read range or data throughput in noisy or metal-rich environments.
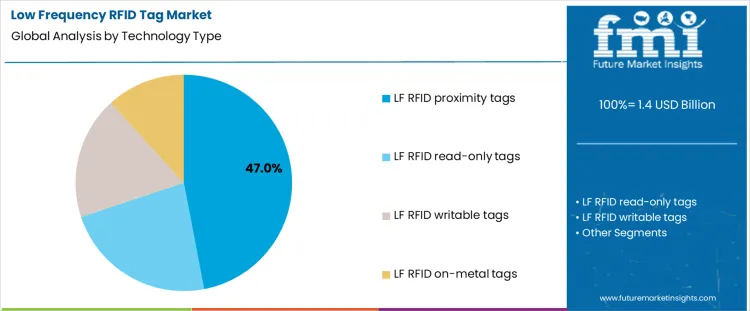
In 2026, LF RFID proximity tags account for approximately 47% of demand, primarily due to the scale and inertia of their installed base. Animal tagging programs, basic access control systems, and legacy industrial identification systems were built around LF proximity technology many years ago and continue to operate using the same architectures. Once deployed, operators typically replace tags with identical formats to avoid changing readers, software, or operating procedures.
Proximity tags also tolerate water, soil, and biological tissue, reinforcing their use in livestock and companion animal identification. This accumulated infrastructure and conservative replacement behavior keep proximity tags at the center of unit volume.
Read-only, read/write, and on-metal tags address more specific requirements. Read/write tags support limited data updates, though many LF systems do not require field rewriting. On-metal tags address installation on tools and equipment but are largely confined to narrower industrial applications. These categories grow where functional needs exist but do not displace the broad proximity tag base embedded in millions of existing systems.
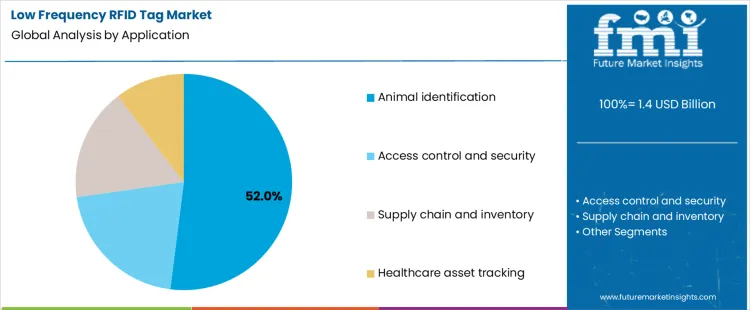
In 2026, animal identification accounts for approximately 52% of demand, as LF RFID remains the standard technology for many livestock and companion animal registration programs. Regulatory frameworks, veterinary practices, and farm management systems in many regions were designed around LF technology due to its strong performance in biological environments. Once identification is mandated, each animal requires a tag, creating large and continuous volume demand. Replacement and new births sustain this base. Low cost and long service life further align with agricultural and veterinary economics.
Access control, supply chain, and healthcare asset tracking follow different adoption paths. Access systems increasingly migrate to higher frequencies for longer range or enhanced security. Supply chain tracking favors UHF RFID for bulk reading, limiting LF usage. Healthcare asset tracking typically applies LF RFID selectively in interference-sensitive zones rather than across entire facilities. While these applications remain important, they are more fragmented. Animal identification, by contrast, is universal within its scope, making it the primary volume driver for LF RFID tags.
The LF RFID tag market is shaped more by how industries regulate identification and tracking than by advances in tag technology. LF RFID remains deeply embedded in applications where reliability near metal, liquids, and harsh environments is more important than speed or distance. Adoption is moderated by integration effort and conservative operational practices.
As organizations move toward standardized identification platforms across sites and processes, LF RFID tags are increasingly specified as part of system architecture rather than treated as standalone consumables. As a result, market demand is driven by compliance programs, asset governance, and platform decisions, with volumes following institutional rollout plans rather than ad hoc purchasing.
Demand is concentrated in regulated and mission-critical environments. Animal identification, access control, healthcare asset tracking, and industrial process control require reliable identification that functions under complex conditions and supports auditable records. In these environments, LF RFID is trusted for its stability and interference tolerance. Once electronic identification is mandated, tags become mandatory inputs rather than optional upgrades. Replacement cycles and geographic expansion drive steady volumes.
The main barrier is system inertia rather than tag performance. LF RFID systems are embedded in long-established workflows, equipment, and databases. Changing them requires coordinated updates to Fixed RFID Reader, software, and processes, introducing operational risk. Many organizations prefer to maintain proven configurations rather than deploy parallel systems or migrate frequencies. Budget holders prioritize core operations over infrastructure changes that do not deliver immediate productivity gains.
The trend is toward controlled identification platforms. Large organizations increasingly define standard tag and reader architectures that can be reused across sites, factories, or facilities. LF RFID tags that meet these standards benefit from repeat orders without repeated evaluation. Procurement shifts toward framework agreements with approved suppliers to ensure continuity and compatibility. While this reduces fragmentation, it increases switching costs and integrates LF RFID tags into long-term identification systems rather than one-off purchases.
| Country | CAGR (%) |
|---|---|
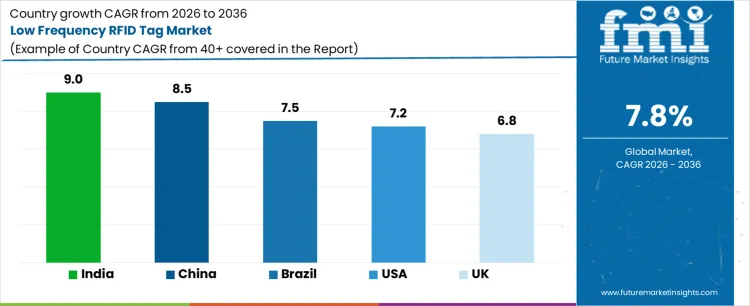
| United States | 7.2% |
| United Kingdom | 6.8% |
| China | 8.5% |
| India | 9.0% |
| Brazil | 7.5% |
Demand for LF RFID tags is rising as industries adopt inventory management, asset tracking, and access control solutions. India leads with a 9.0% CAGR, driven by manufacturing, logistics, and retail adoption. China follows at 8.5%, supported by industrial automation and supply chain optimization. Brazil grows at 7.5%, driven by logistics and manufacturing. The United States grows at 7.2%, supported by inventory and asset management integration. The United Kingdom’s 6.8% CAGR reflects steady adoption in commercial and industrial sectors.
Competition in the LF RFID tag market centers on reliability, read performance, and compatibility with access control, animal identification, and asset tracking systems. Zebra Technologies offers LF RFID tags and encoders designed for stable performance and integration with its printing and scanning platforms. HID Global supplies LF tags optimized for secure access control and credential management interoperability. Alien Technology develops tag chips and inlays with stable performance in complex environments. Impinj provides RFID solutions with ecosystem support and device-level integration for scalable deployments. NXP Semiconductors supplies LF RFID integrated circuits that support interoperability and reliable field performance.
Smartrac (Avery Dennison) delivers application-specific inlays and finished tags for animal identification and industrial tracking, emphasizing supply chain flexibility. GAO RFID offers cost-effective LF tags and readers for asset tracking and identification. Other regional and niche suppliers focus on customized form factors, ruggedized packaging for harsh environments, or sensor-integrated designs. Competitive differentiation is driven by durability, form-factor diversity, read stability, manufacturing quality, and compliance with global LF RFID standards. Suppliers that support comprehensive ecosystems, documentation, and end-user system integration are best positioned to attract buyers in logistics, access control, and livestock management.
RFID tester market forecast from 2025 to 2035, covering market size, CAGR, applications, frequency bands, regional growth, and competitive landscape.
MoreAn in-depth analysis of the global RFID market from 2024 to 2031, covering technology evolution, market structure, passive vs active RFID, and real-world adoption trends.
MoreThe global RFID-enabled gift box market is projected to grow from USD 308.3 million in 2026 to USD 480.7 million by 2036 at a 4.5% CAGR. Explore market outlook, application demand, product types, country-level growth, and key packaging companies s...
MoreAn in-depth look at the RFID printer market from 2025 to 2035, covering growth drivers, risks, regional trends, and real-world adoption across key industries.
More