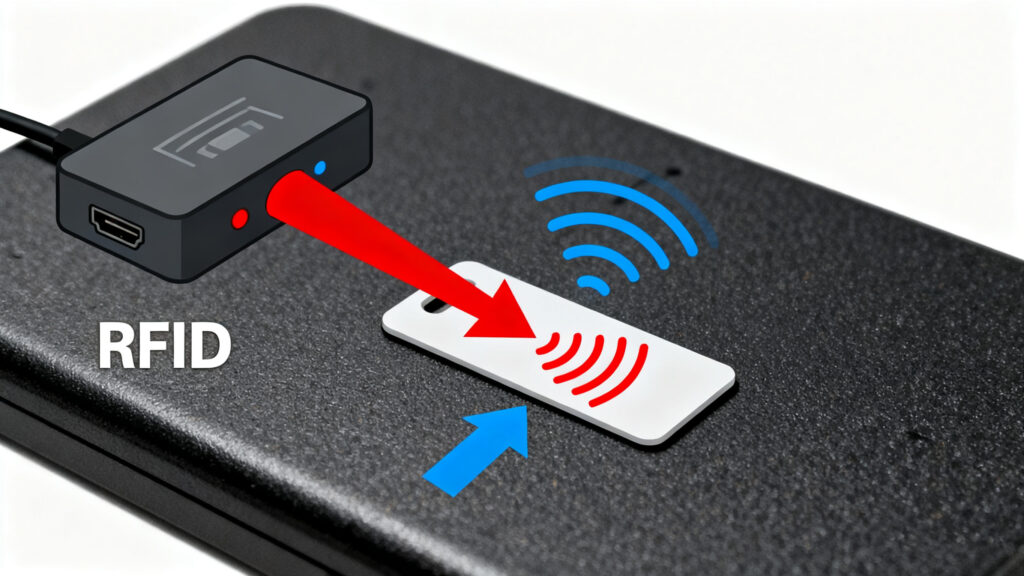
Can a Smartphone Read RFID?
102Thinking of using your phone as a scanner? We answer "can a smartphone read RFID" and explain the major technical and practical limitations for business use.
MoreAll RFID Product
If you’ve ever wondered how stores, libraries, or warehouses keep track of items without scanning barcodes one by one, passive RFID tags are often the secret behind it. They may look like tiny stickers or small cards, but they pack a clever trick: they work without a battery.
A passive RFID tag is basically a small chip attached to an antenna. Unlike active RFID tags, it doesn’t have its own power source. Instead, it “borrows” energy from an RFID reader nearby to function. This makes it super cheap, long-lasting, and maintenance-free—perfect for libraries, warehouses, and retail.
Here’s the simple version:

So, the tag works entirely off the energy from the reader—no batteries required.
Passive RFID tags are popular because they make tracking items fast and efficient:
So, next time you borrow a book from a library or notice a store tracking items without scanning barcodes, you’re probably seeing passive RFID tags in action. They are small, clever, and surprisingly efficient: they capture energy from a reader, send back information, and make item tracking simple and quick.
Simply put: passive RFID tags work by using the reader’s energy to power themselves and communicate wirelessly—no battery needed.
CYKEO Passive RFID Tags are made for wet and high-humidity environments where standard labels do not last. This rfid passive tag is often used around liquids, chemicals and temperature changes, providing stable reading distance and long data life for industrial tracking.
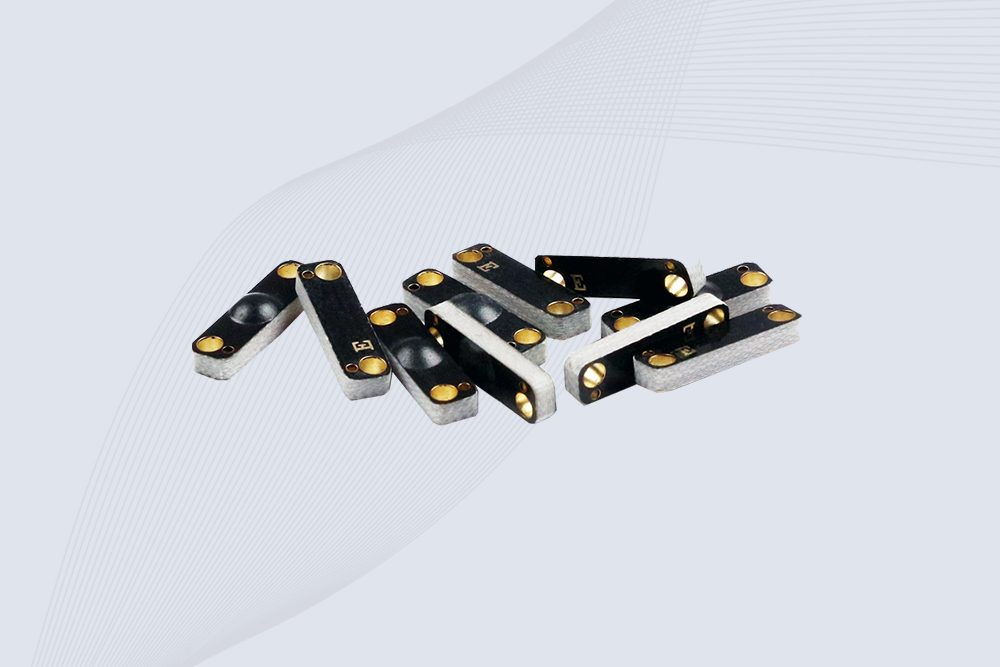

CYKEO CK-BQ1504 Metal RFID Tags is a compact anti-metal UHF RFID solution built for direct mounting on metal surfaces. With stable 8-meter read range, Ucode-8 chip, and long data retention, this rfid metal tag fits tools, containers, automotive parts, and industrial asset tracking.
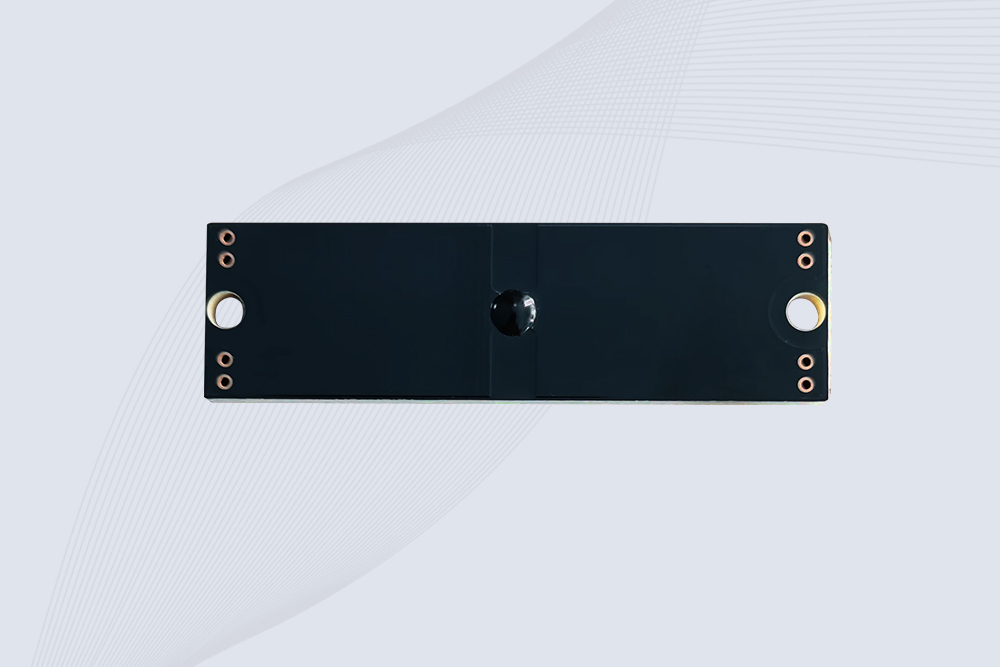

CYKEO CK-BQ7020 On-Metal RFID Tags are designed for reliable tracking on steel and metal surfaces. Built with an FR4 epoxy body and industrial-grade chips, these On-Metal RFID Tags deliver stable performance, long data life, and chemical resistance, making them a dependable RFID anti-metal tag for harsh environments.
The CYKEO CK-BQ6025 Anti-Metal RFID Tag is built for metal surfaces where standard tags fail. Designed for long-range performance, harsh environments, and stable data retention, this Anti-Metal RFID Tag is ideal for industrial assets, containers, and equipment tracking using on metal RFID tags.
Thinking of using your phone as a scanner? We answer "can a smartphone read RFID" and explain the major technical and practical limitations for business use.
MoreTrying to understand what an RFID Intelligent Police Equipment Cabinet really solves? This real-world breakdown covers police gear management, law enforcement storage workflows, keyless RFID locker systems, and smart cabinet setups — including wha...
MoreDiscover how RFID for tool tracking enhances safety, compliance, and efficiency in high-risk industries. Learn about Cykeo’s automated solutions.
MoreCan RFID reader read credit cards? We explain the technology compatibility, security protections, and key differences between payment and industrial RFID systems.
More