Can iPhone Read RFID Chips? The Chip-Level Truth
67Can iPhone read RFID chips? We explain which embedded chips work with iPhone NFC and which don't—plus when you need industrial RFID solutions.
MoreAll RFID Product
Think of RFID as giving every box, pallet, or even single product a “voice.” Instead of workers scanning barcodes one by one, RFID tags allow items to be identified automatically through radio signals. When forklifts drive past readers or goods pass through dock doors, the system instantly knows what’s moving, where it’s going, and whether it’s in the right place.
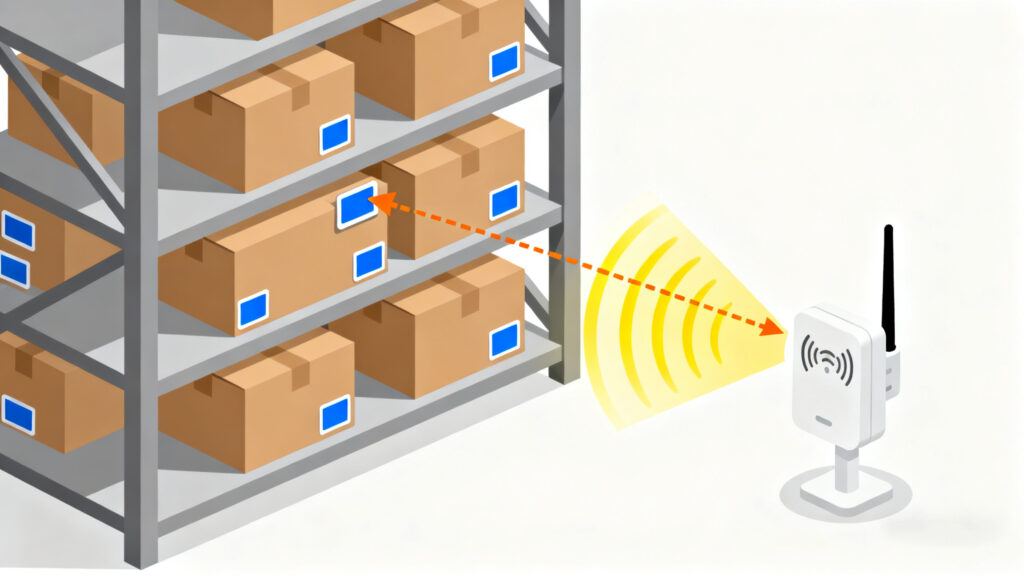
Barcodes are like nametags—you have to point a scanner directly at them to read. RFID, on the other hand, works more like Wi-Fi; it can pick up signals without direct line-of-sight. That means dozens or even hundreds of items can be identified at once, even if they’re stacked inside a carton or sitting on a high shelf.
Not necessarily. Many warehouses start small, maybe just by adding RFID gates at receiving docks or equipping forklifts with readers. Over time, they can expand to cover picking, inventory checks, and even automated shipping verification. The key is that RFID adapts—you don’t have to rebuild the whole warehouse to get started.
No, even smaller warehouses benefit. For example, a mid-sized operation that struggles with misplaced items can use RFID shelves or handheld readers to cut down search times. Larger facilities often see bigger gains because of the scale, but the technology scales both ways.
Accuracy depends on tag quality, placement, and the reader setup. In a well-designed system, read rates can exceed 95–99%. But it’s not magic—metal surfaces, liquids, and interference can sometimes block signals. Warehouses usually adjust by using different types of tags or installing more readers in tricky areas.
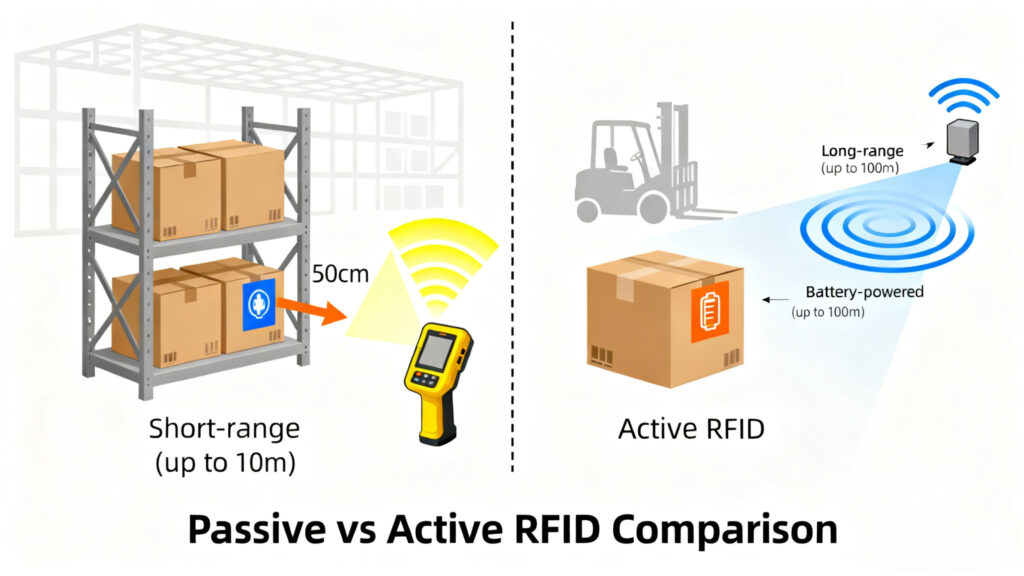
Yes, but with nuance. Passive RFID gives snapshots—items are read when passing a gate or scanned by a handheld. Active RFID, which has its own battery, can provide continuous location tracking like GPS inside the warehouse. Companies often mix both depending on how precise they need to be.
RFID isn’t cheap upfront, especially if thousands of tags and multiple readers are involved. But warehouses that adopt it often find the savings in labor, fewer errors, and better inventory accuracy cover the investment. Think fewer “lost” pallets, faster cycle counts, and smoother order fulfillment.
Most RFID systems are designed to plug into WMS (Warehouse Management Systems) or ERP platforms. When a pallet is tagged and scanned, the system updates inventory records instantly. That means managers see real-time stock levels without sending someone to count manually.
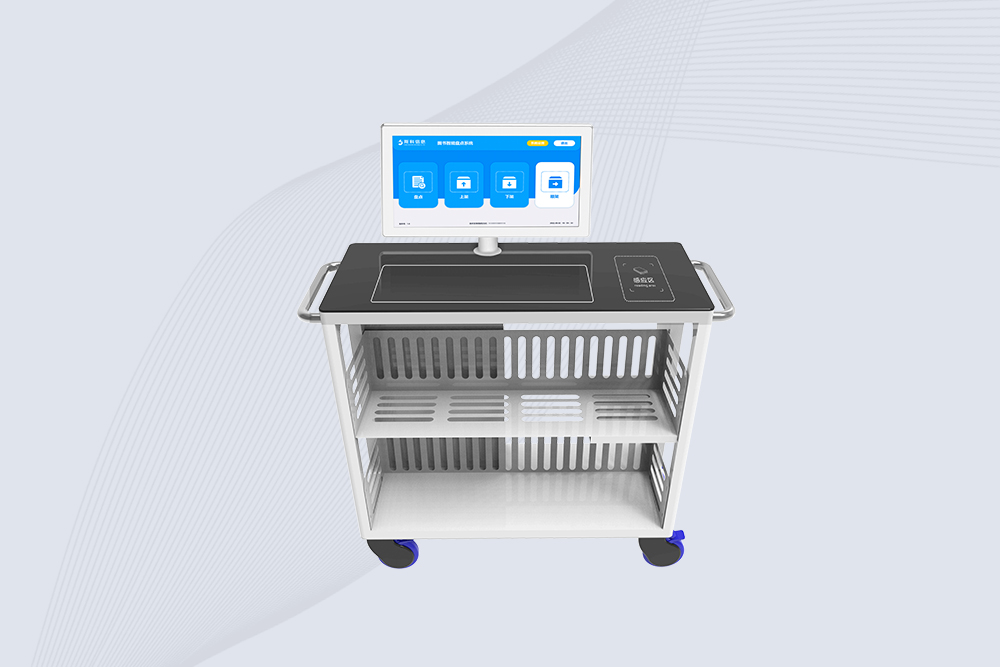

Cykeo CYKEO-C2 UHF RFID inventory cart features 10 UHF readers, 500 tags/sec scanning, Windows/Android OS, and hybrid power for warehouses/libraries. Supports ISO 18000-6C protocols and customization.
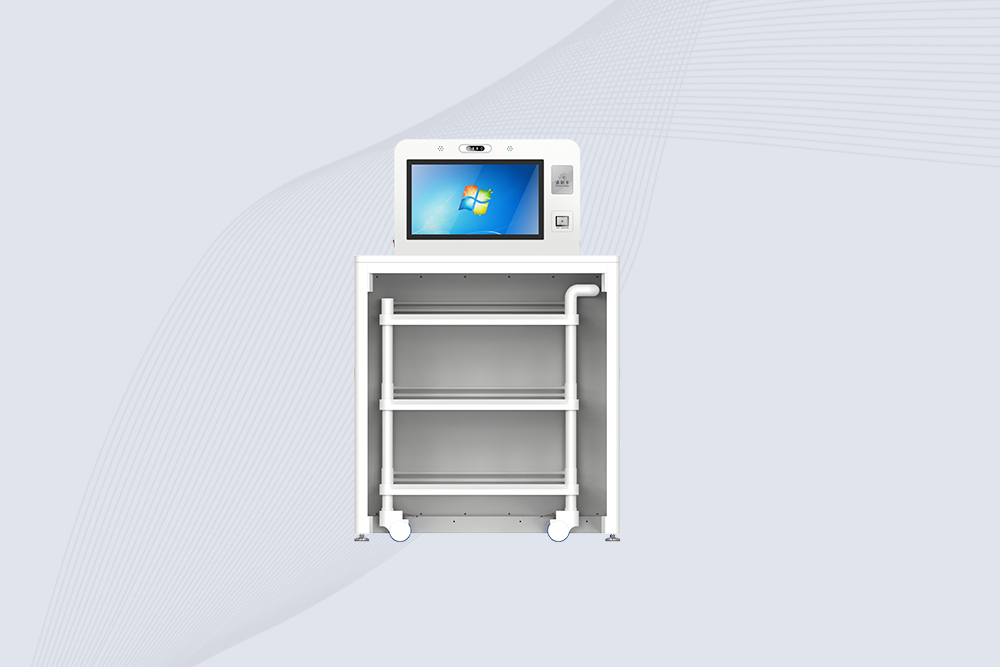

Cykeo’s industrial RFID Inventory Tracking station features dual scanning modes, 200+ items/sec bulk reading, and SAP integration for precise warehouse management. MIL-STD-810G certified with Windows/Android OS.

Cykeo CK-D7L RFID system for inventory offers 40+ tags/sec scanning, 150L secure storage, and Impinj R2000 chipset for warehouses, toolrooms, and retail. Global frequency compliance (840-960MHz).
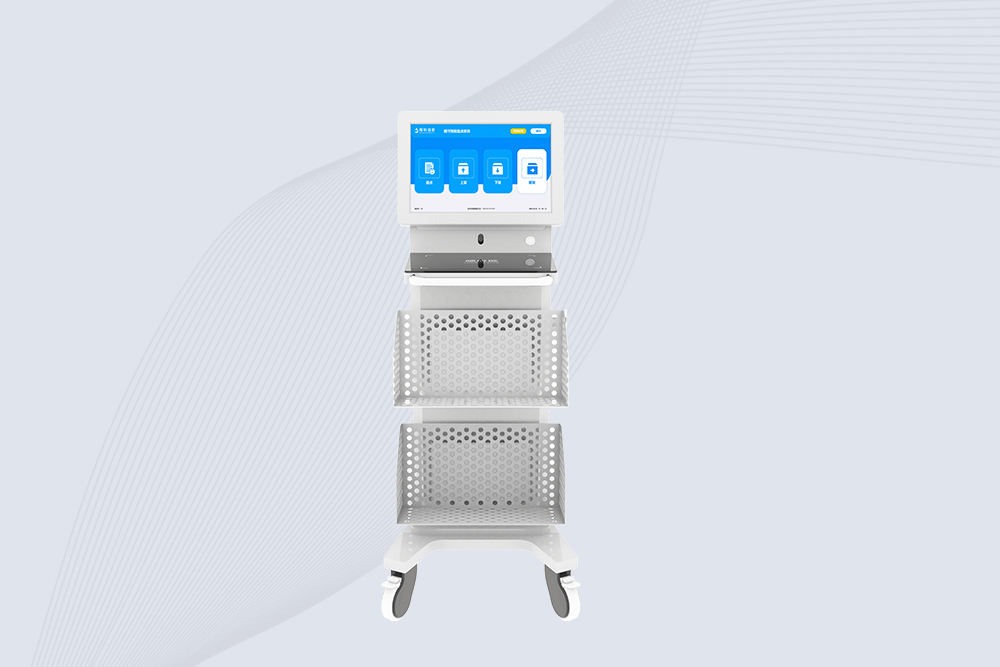

Cykeo CYKEO-C1 mobile RFID scanner cart features PLC-controlled antenna lifting, 10-tag/sec reading, and 21.5″ touchscreen for libraries, hospitals, and warehouses. Supports Windows/Android and multi-protocol RFID.
Can iPhone read RFID chips? We explain which embedded chips work with iPhone NFC and which don't—plus when you need industrial RFID solutions.
MoreCompare passive and active RFID tags: costs, range, and use cases. Discover which system (passive or active RFID) fits logistics, healthcare, or industrial tracking.
MoreDiscover how RFID key management systems work, their benefits, and why businesses choose RFID technology for secure, efficient, and automated key control.
MoreWondering if RFID can read credit cards? We explain how contactless payment works, the security built in, and the key differences from standard RFID tracking.
More