Can Fixed RFID Readers Withstand Extreme Temperatures?
1137Discover if fixed RFID readers can operate in extreme temperatures. Learn how Cykeo’s industrial-grade solutions handle freezing cold, intense heat, and harsh environments.
MoreAll RFID Product
A wireless RFID scanner is a portable device capable of reading RFID tag information without physical contact. It typically communicates with a host device via Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, or USB. Combining RFID technology with wireless connectivity, these scanners are widely used in mobile asset management, inventory checks, inspection tasks, and more.
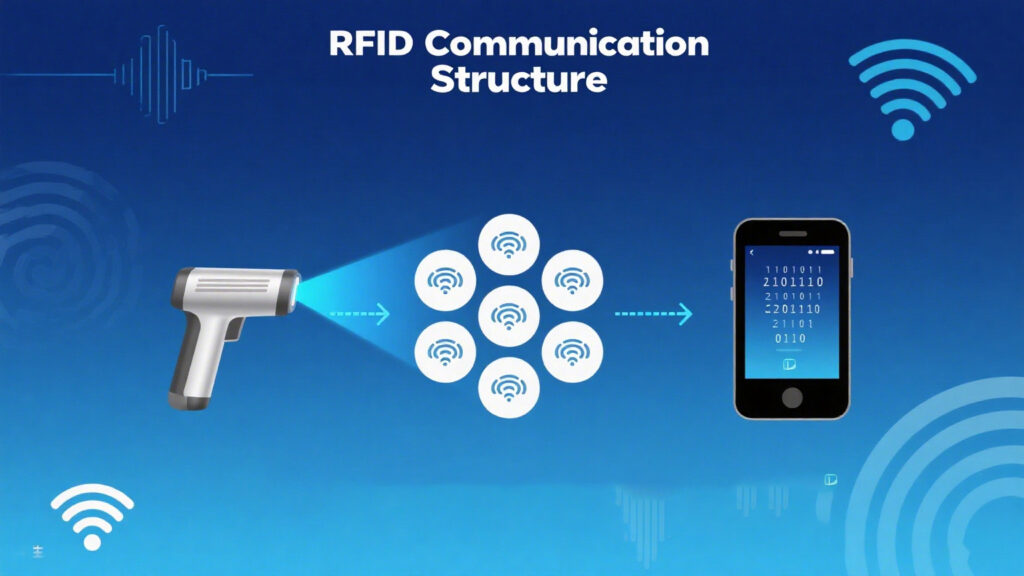
Wireless RFID scanners emit radio frequency signals via their antenna to activate RFID tags (either passive or active) and receive the returned data. The scanner then transmits the data wirelessly to a PC, smartphone, or cloud platform to complete the identification and logging process.
Common frequency bands include:
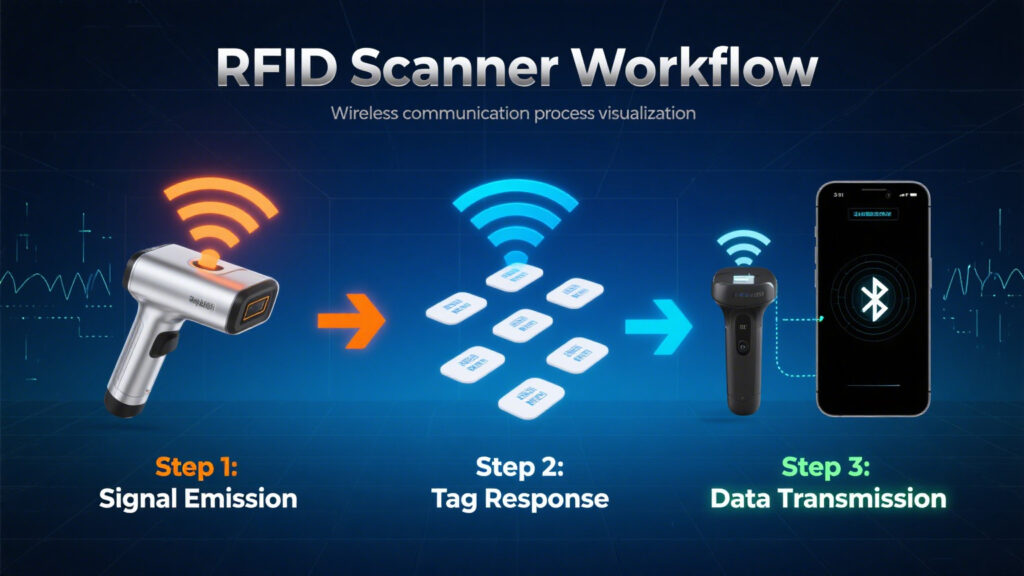
Typical features of wireless RFID scanners include:
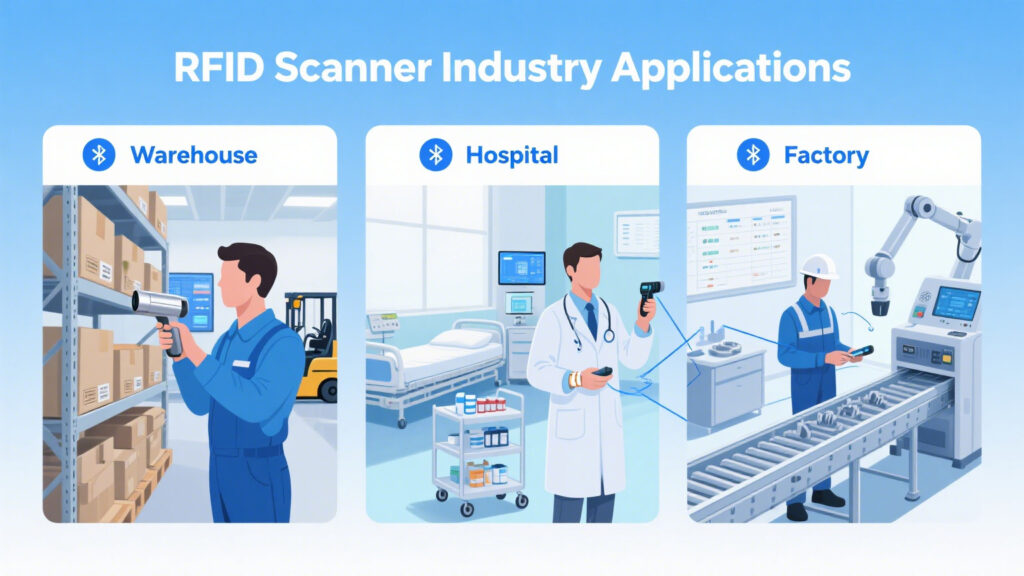
Wireless RFID scanners are used across a wide range of industries and scenarios, such as:
When selecting a suitable device, consider the following factors:
Thanks to their flexibility, efficiency, and multi-functionality, wireless RFID scanners have become an ideal solution for modern asset tracking and mobile identification. Businesses should choose devices based on their application scenarios, budget, system compatibility, and technical requirements. With the growth of IoT and cloud platforms, wireless RFID scanning technology will continue to evolve toward greater intelligence and automation.

Cykeo CYKEO-B5L portable iPhone RFID reader features 8m range, 500 tags/sec scanning, and built-in 10000mAh charger. Perfect for retail/warehouse teams needing iOS integration.

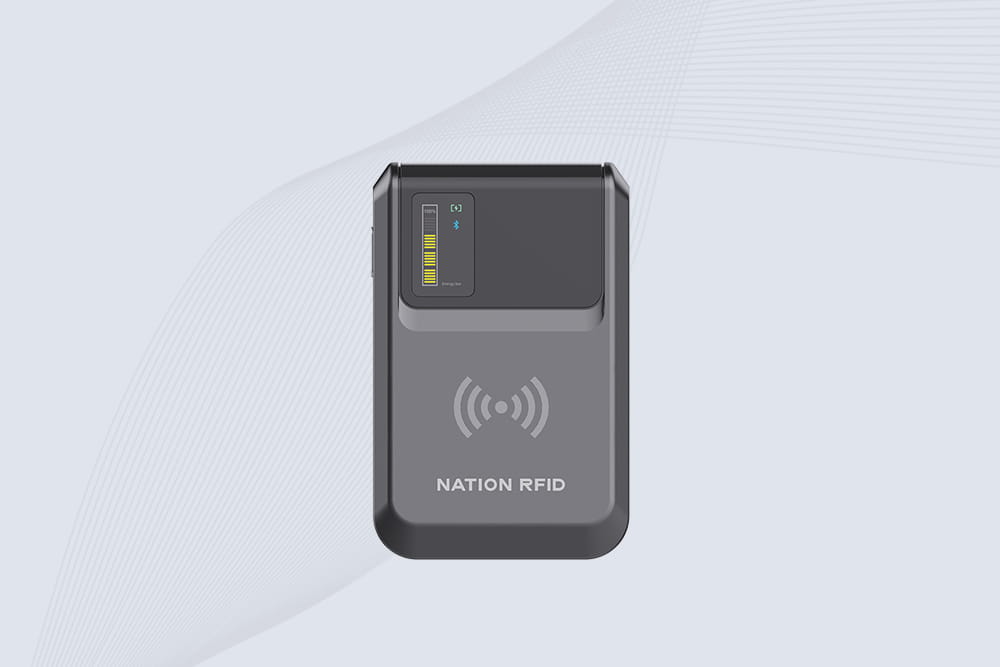
Cykeo CYKEO-B4L Android RFID reader features 37g magnetic phone attachment, 30cm UHF scanning, and Java/C# SDK for mobile asset tracking. Ideal for anti-counterfeit and warehouse verification.
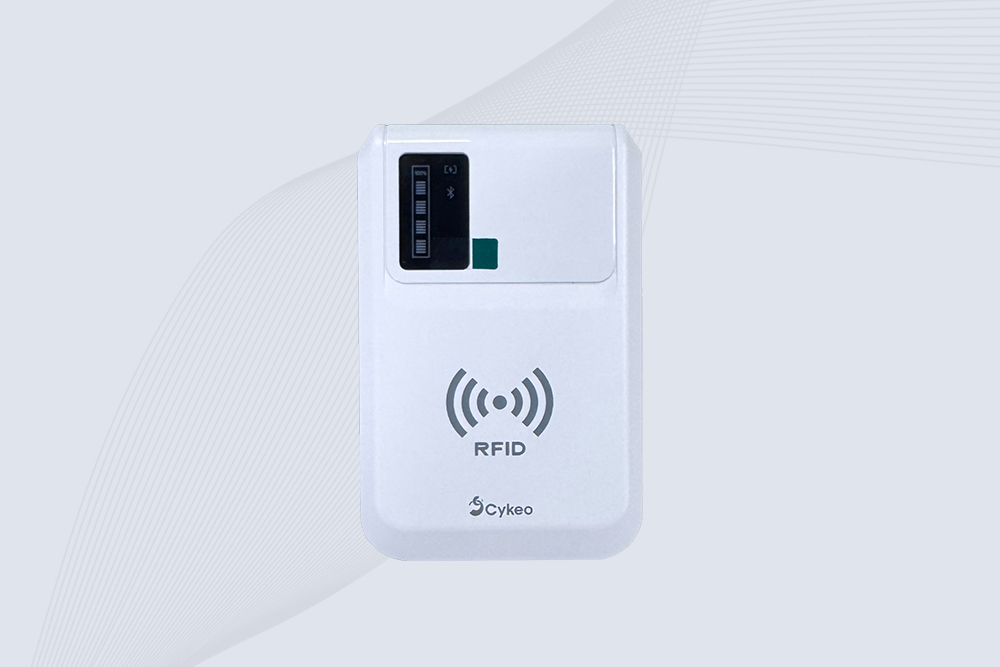

CYKEO CYKEO-B5L RFID Chip Reader iPhone delivers long-range UHF scanning, iOS compatibility, and all-day battery life. A compact RFID Tag Reader iPhone solution for retail, healthcare, and mobile inventory tracking.
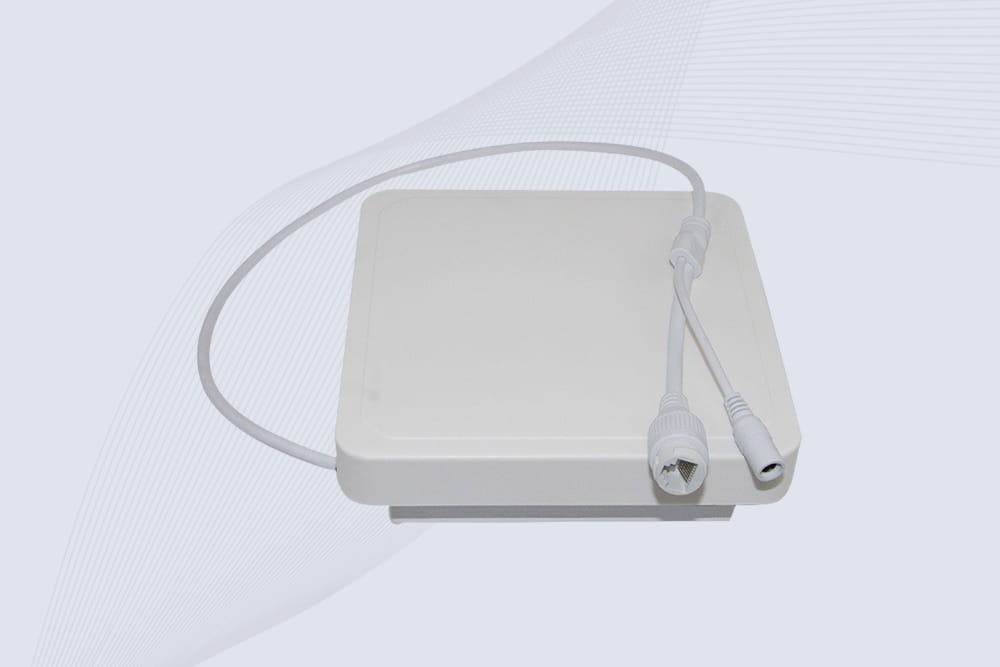

Cykeo’s industrial long range RFID reader delivers 20-meter scanning, 500+ tags/sec speed, and IP67 waterproof design for automated warehouses, logistics, and harsh environment applications.
Discover if fixed RFID readers can operate in extreme temperatures. Learn how Cykeo’s industrial-grade solutions handle freezing cold, intense heat, and harsh environments.
MoreFix RFID antenna signal issues in metal-heavy environments like warehouses and factories. Learn about anti-metal tags, antenna positioning, and interference mitigation.
MoreDiscover the most durable RFID handheld readers for construction sites. Explore rugged features, weather resistance, and Cykeo’s solutions for harsh environments.
MoreUnderstand how security tag readers function and compare the advantages of RFID and magnetic systems to help you choose the right anti-theft tag reading technology for your business.
More