RFID Multiple Tag Reading: Hitting 200+ Tags/Min in Real Warehouses
165RFID multiple tag reading tested: Discover real-world speeds, interference solutions, and how Cykeo users scan pallets in seconds. No hype - just warehouse results.
MoreAll RFID Product
When it comes to medical asset management, relying solely on traditional spreadsheets and manual inventory is way behind the times. Once hospital equipment piles up — just the infusion pumps run into the hundreds — you gotta bring in some high-tech help or you’re not gonna keep up. RFID sounds fancy, but it’s no magic wand; you’ve gotta fit it to the actual on-site situation for it to work.
Real-time Asset Tracking — It’s Not Just “Slap a Tag On”
Anyone in the tech field knows just stickingRFID tag on equipment isn’t straightforward in practice. We once had tags stuck on stainless steel infusion pumps where the signals got completely “shielded” — the readers couldn’t pick them up at all. Later we switched to special “metal-resistant” tags and added more antennas strategically; only then did the reading distance stabilize at about 3 meters. Don’t get fooled by vendors claiming “10 meters no problem” — the magnetic environment and equipment density on site hugely affect performance.
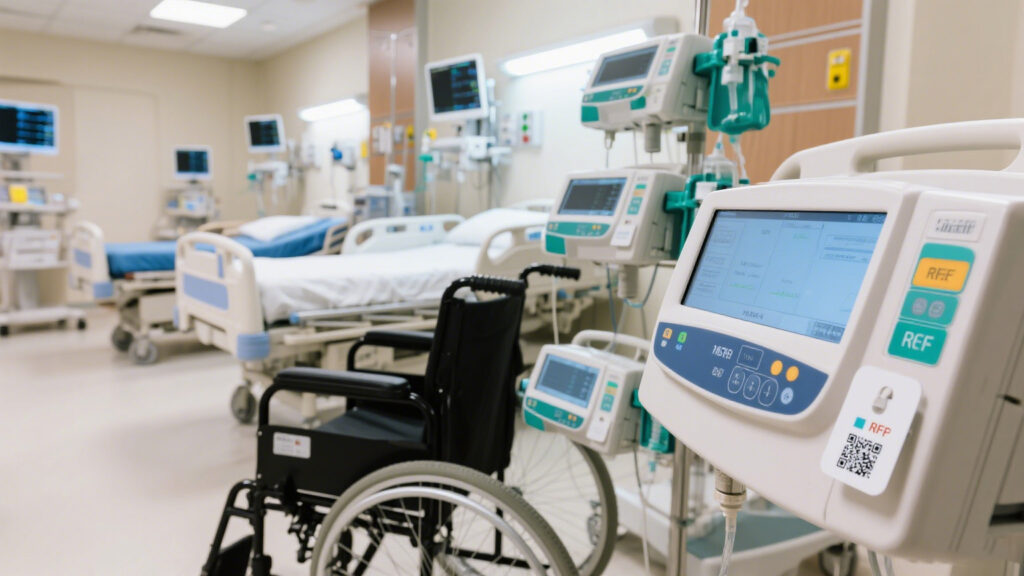
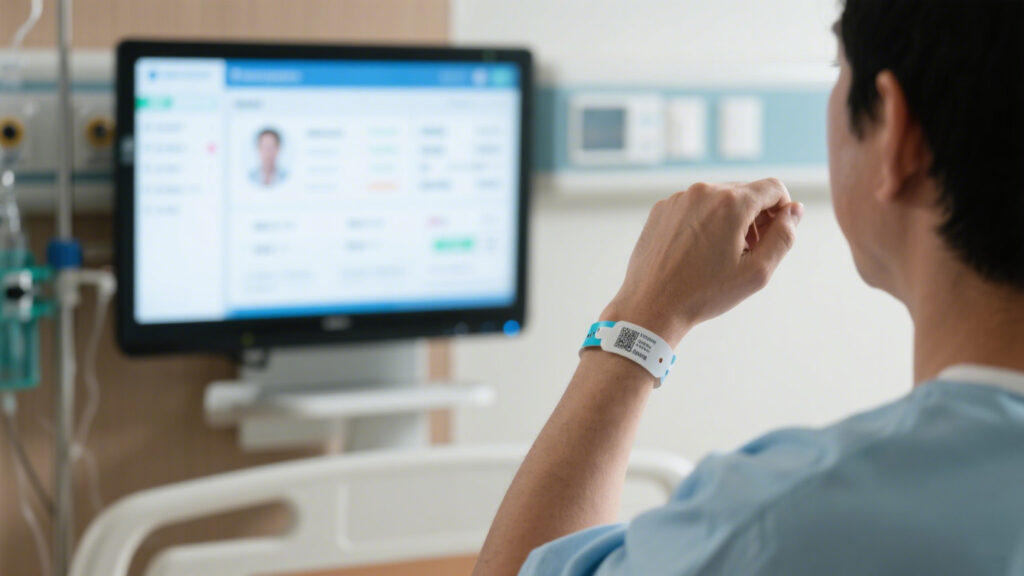
Hospitals put RFID wristbands on patients intending to prevent identity mix-ups and reduce medication errors. But I visited a top-tier hospital where they still didn’t fully trust the system. The system sometimes missed reads, so nurses had to double-check multiple times, which ironically added to their workload.
Also, patients refusing to keep wristbands on, or accidentally swapping them, happens often, leading to inaccurate data. You can see there’s still a gap between “smart management” and reality. Patient safety still depends heavily on nurses’ experience, with RFID as just an assistant, not a savior.
Ideally, RFID systems run fully automatically. But during hospital pilots, we found interfaces weren’t flexible enough, integration with the hospital’s existing HIS (Hospital Information System) was tricky, and even a 1-minute delay in data sync caused complaints from nurses about sluggish devices. The “API flexibility” and “real-time capability” often become sticking points in medical applications. Without those, talk of “seamless integration” is just hot air.

Cost is the hospital’s biggest concern. One private hospital installed an RFID asset management system claiming to save 20% on procurement. But after six months, maintenance and training costs had doubled, and while equipment management became more systematic, the “savings” weren’t that obvious.
RFID systems are far more than just putting on tags. At a large medical device supplier site, we spent over two months from tag selection, reader layout, software customization, to staff training — every step full of pitfalls.
The biggest headache is people: the gap between tech staff’s understanding and nurses’ actual operations often caused project delays. Plus, hospitals’ old power and wireless infrastructure created interference issues. If tuning wasn’t done well, the blame would fall on tag performance — this finger-pointing is an industry-wide problem.
RFID for medical asset management is definitely the future, but don’t expect “install and forget.” Every hospital’s environment, staff, and equipment are different; a one-size-fits-all approach won’t cut it.
A truly effective system depends on the “on-site tuning + software customization + ongoing training” trinity. RFID projects are 90% debugging, 10% selling tags.

Cykeo CK-BQ6826 Jewelry uhf rfid tag features NXP UCODE 9, 8m read range on metal, and anti-counterfeit security for luxury assets.

Cykeo CK-BQ8554HF HF rfid cards feature FM1108 chip, 100K write cycles, and customizable printing for access control systems.

Cykeo CK-BQ8554UHF uhf rfid card features U9 chip, 100K write cycles, and CR80 size for access control/inventory management.
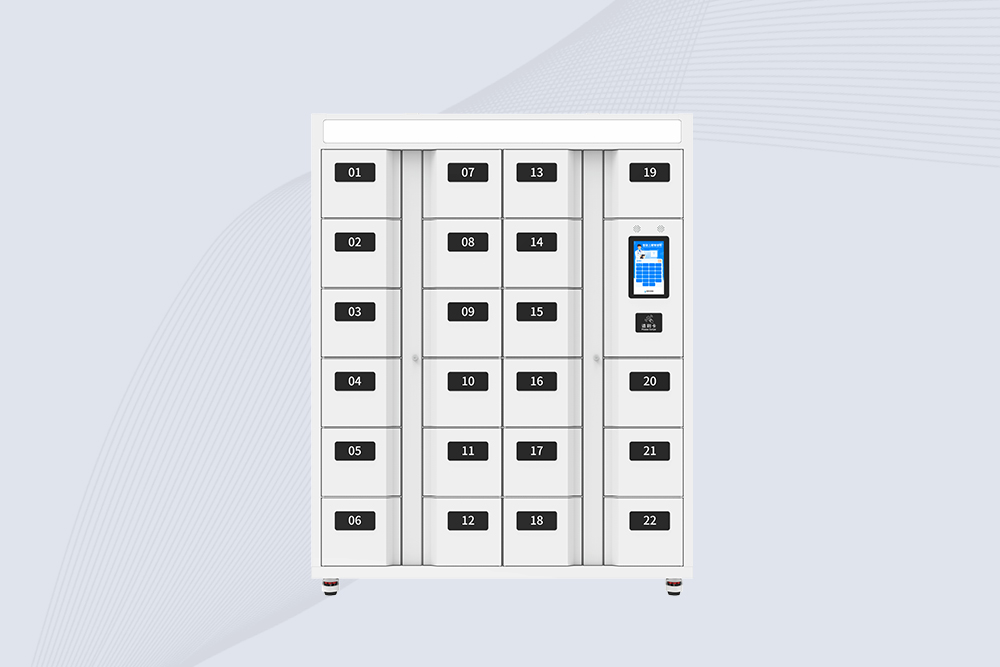

Cykeo CK-G2224 rfid linen management cabinet features modular lockers, 10.1″ Android screen, and 200+/sec scanning for hospitals/hotels. SAP/Oracle integration.
RFID multiple tag reading tested: Discover real-world speeds, interference solutions, and how Cykeo users scan pallets in seconds. No hype - just warehouse results.
MoreNeed to track tools across sprawling construction sites? Discover rugged UHF RFID readers that survive dust, rain, and chaos while scanning up to 100 ft.
More125kHz RFID reader, with its unique performance characteristics, plays an irreplaceable role in many use cases.
MoreCykeo RFID Medical Equipment Management System enables hospitals to achieve automatic device identification, real-time location tracking, fast inventory checks, and full-process intelligent management—an ideal solution for secure and efficient med...
More