Affordable RFID Antenna Solutions for SMBs: Maximize ROI Without Breaking the Bank
698Discover budget-friendly RFID antenna strategies for small to medium businesses. Cut costs, boost accuracy, and scale your operations efficiently.
MoreAll RFID Product
If you’ve ever worked in a warehouse, managed a hospital’s equipment, or handled construction tools, you probably know how easy it is for assets to “disappear.” Sometimes it’s human error, sometimes it’s just chaos. That’s where the RFID tag tracking system quietly steps in — not as a buzzword, but as a practical solution that keeps things visible, traceable, and accountable.
At its core, an RFID tag tracking system is a combination of small electronic tags, antennas, and readers that work together to identify and track items automatically through radio waves. Each RFID tag carries a unique ID, like a digital fingerprint. When the tag comes within range of a reader, it sends back information that gets captured into a management system — no scanning, no line of sight needed.
In simple terms: you tag it once, and the system keeps an eye on it for you.
The workflow is pretty straightforward:
It’s the same principle behind airport luggage tracking or warehouse automation — only tailored to whatever industry needs visibility the most.
Not all tags are created equal, and choosing the right one depends on what you’re tracking and where.
Think of it this way: passive tags “listen,” active tags “speak,” and semi-passive tags “whisper when needed.”
The radio frequency used in an RFID tag tracking system determines how it behaves in real-world environments.
In short, LF works best when reliability matters, HF when accuracy counts, and UHF when scale is everything.
You might wonder: if barcodes already work, why switch?
Here’s the difference — RFID doesn’t need a line of sight. You can read dozens or even hundreds of items at once, through boxes or containers. The tags store more data, last longer, and don’t wear out from friction or sunlight.
Imagine scanning 500 tools in under 10 seconds without lifting a single one. That’s the kind of automation RFID makes possible.
Of course, it’s not all magic. RFID systems have their own challenges:
But once deployed properly, the payoff is significant: fewer losses, faster audits, and a clear map of where everything is.
Across industries, RFID tag tracking systems are quietly reshaping operations:
Each case proves one simple truth: visibility equals control.
In an era where data drives every decision, RFID brings physical assets into the digital world. It closes the gap between what’s on your books and what’s actually on the floor. And unlike manual systems, it doesn’t rely on someone remembering to scan or write things down.
That’s what makes RFID more than just a tracking tool — it’s a foundation for smarter, more accountable operations.
An RFID tag tracking system isn’t about fancy tech — it’s about clarity. It’s about knowing what you own, where it is, and how it’s being used. Whether you’re managing 50 laptops or 50,000 containers, the idea is the same: the less time you spend looking for things, the more time you have to actually use them.
In the end, RFID doesn’t just track assets — it gives businesses their visibility back.
CYKEO Passive RFID Tags are made for wet and high-humidity environments where standard labels do not last. This rfid passive tag is often used around liquids, chemicals and temperature changes, providing stable reading distance and long data life for industrial tracking.
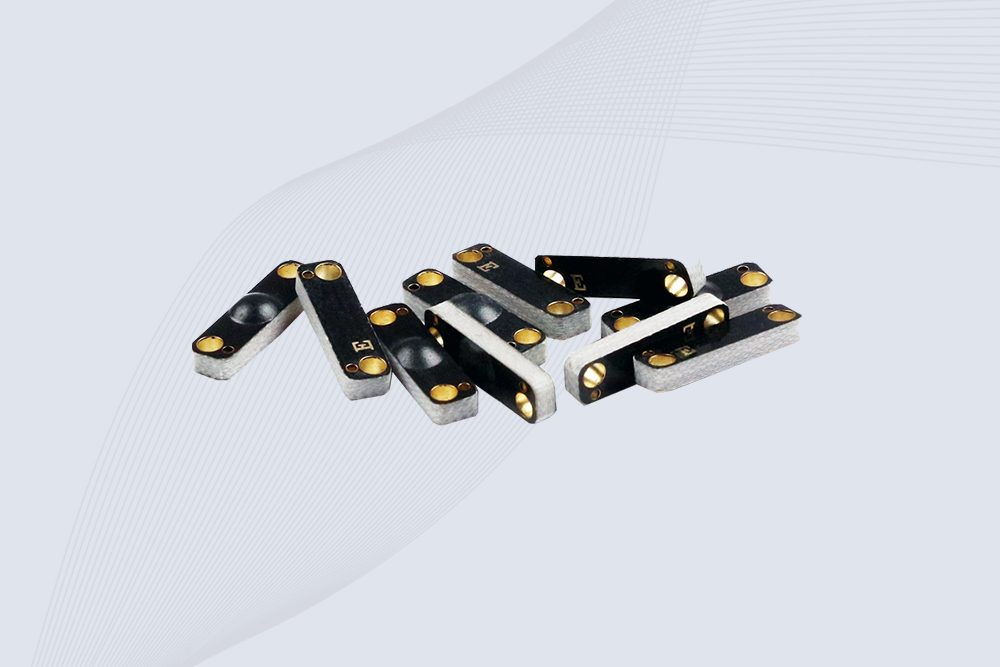

CYKEO CK-BQ1504 Metal RFID Tags is a compact anti-metal UHF RFID solution built for direct mounting on metal surfaces. With stable 8-meter read range, Ucode-8 chip, and long data retention, this rfid metal tag fits tools, containers, automotive parts, and industrial asset tracking.
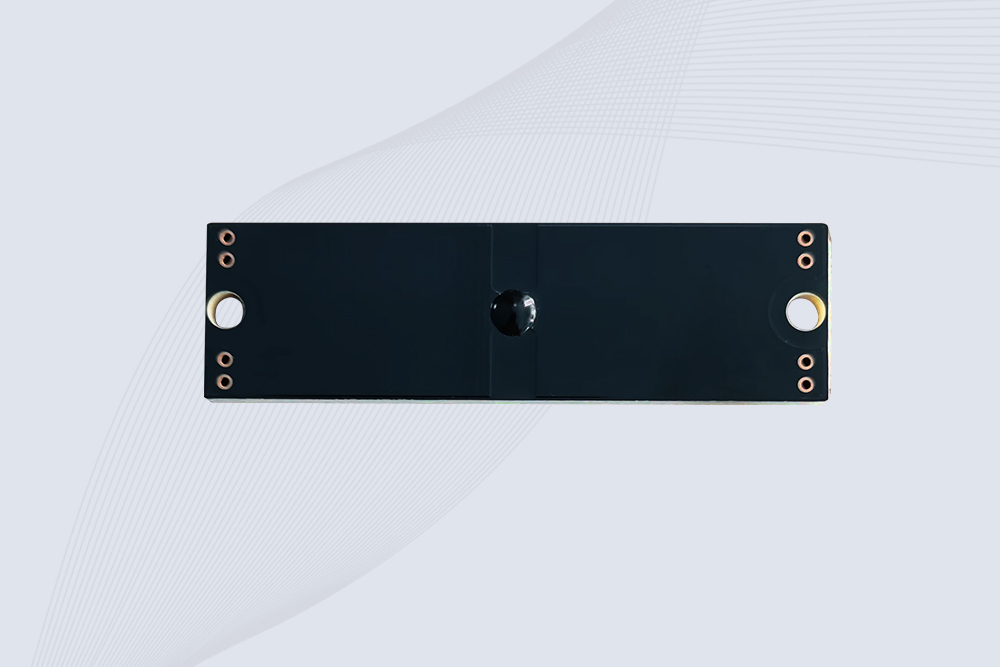

CYKEO CK-BQ7020 On-Metal RFID Tags are designed for reliable tracking on steel and metal surfaces. Built with an FR4 epoxy body and industrial-grade chips, these On-Metal RFID Tags deliver stable performance, long data life, and chemical resistance, making them a dependable RFID anti-metal tag for harsh environments.
The CYKEO CK-BQ6025 Anti-Metal RFID Tag is built for metal surfaces where standard tags fail. Designed for long-range performance, harsh environments, and stable data retention, this Anti-Metal RFID Tag is ideal for industrial assets, containers, and equipment tracking using on metal RFID tags.
Discover budget-friendly RFID antenna strategies for small to medium businesses. Cut costs, boost accuracy, and scale your operations efficiently.
Morelong-range UHF RFID readers that scan tags from up to 20 meters. Cykeo CK‑RA4L, CK‑RA6L, CK‑RA9L, and CK‑RA12L handle high-speed batch reading, work in tough industrial environments, and easily integrate with WMS, ERP, and IoT systems.
MoreDiscover which is more expensive, RFID or barcode. We break down costs, use cases, and long-term savings for inventory management. Make informed decisions for your business.
MoreRFID tags are everywhere—from the clothes you try on to the packages moving through ports. Explore how RFID tags work, their hidden power in logistics, healthcare, retail, and beyond, with real-world reflections and human insight.
More